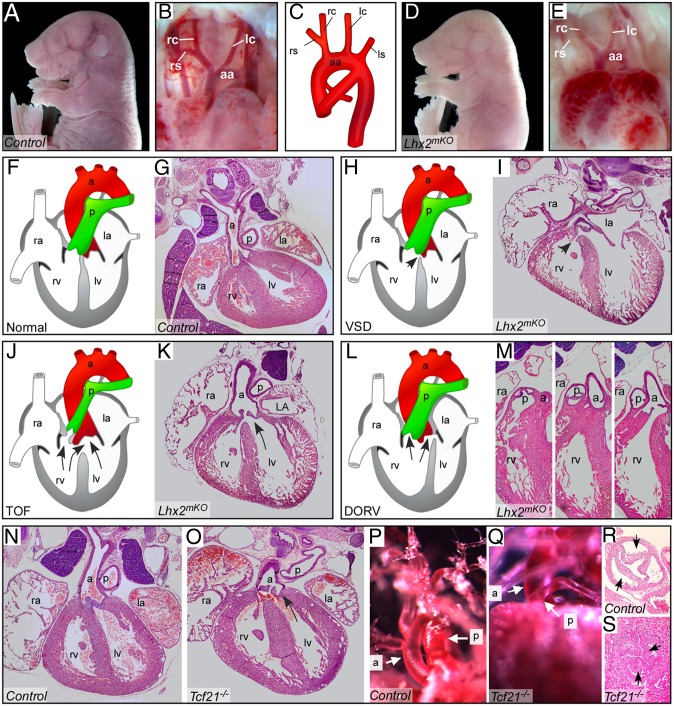
Fig. 5.
Lhx2 and Tcf21 mutant embryos display specific DGS-like cardiac defects. (A–E) Whole-mount E17.5 controls (A and B) and Lhx2mKO mutants (D and E), both displaying normally shaped aortic arches (B and D, respectively). Note severe anemia in the mutant (D) embryo, compared with control (A). A scheme illustrating the normal configuration of the aortic arch (C). (F and G) H&E staining of heart paraffin sections in control hearts. (F–M) Lhx2mKO mutants display a simple VSD (H and I, arrow), schematically illustrated (H); tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), characterized by both VSD and overriding aorta (J and K, arrows); double-outlet right ventricle (DORV) (L and M). (N–S) E17.5 Tcf21 mutant embryos display TOF, VSD, and overriding aorta (O) compared with a control heart (N). In addition E17.5 Tcf21 mutant embryos have pulmonic stenosis, shown by vascular casting (Q) and H&E staining (S) compared with controls (P and R, respectively). a, aorta; aa, aortic arch; ls, left subclavian artery; lc, left common carotid artery; la, left atrium; lv, left ventricle; p, pulmonary artery; ra, right atrium rc, right common carotid artery; rs, right subclavian artery; rv, right ventricle. The left side of the mouse is displayed on the right side of the picture in all panels.