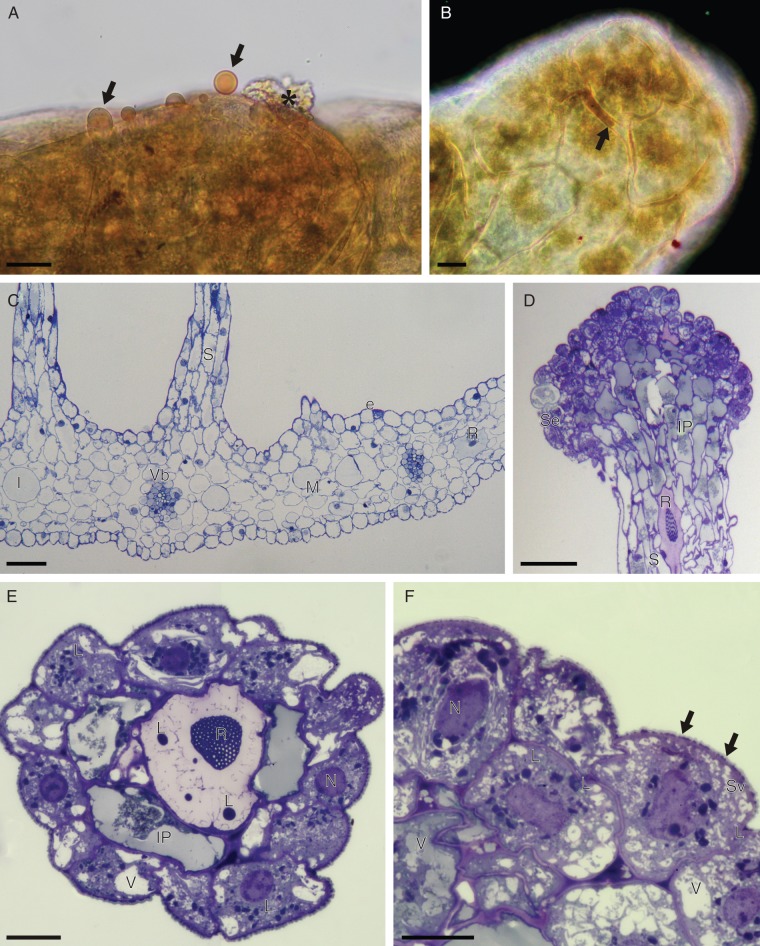
Fig. 4.
(A, B) Detail of head of labellar osmophore of C. membranacea, treated with Sudan III (LM). (A) Osmophore tissue with secreted lipid droplets (arrows) that stain orange-red with Sudan III; also note the secretory residues (asterisk) present on the osmophore surface. (B) Surface view of osmophore head showing the accumulation of secreted lipid material between isodiametric cells (arrow). Note that the cuticle also stains red with Sudan III. (C–F) Labellar anatomy of C. membranacea (LM). (C) Transverse section of labellum with bases of stalked osmophores and collateral vascular bundles. (D) Vertical section through apex of osmophore showing head comprising intensely stained secretory cells and subsecretory layer containing amorphous, intravacuolar precipitates. The stalk contains idioblasts with raphides. (E) Transverse section of osmophore showing outer layer of secretory cells, subsecretory layer with intravacuolar precipitates, and a central cell with intravacuolar raphides and spherical lipid bodies. (F) Detail of secetory cells with perinuclear plastids. Note the vesicles that aggregate close to the cell wall and the lipid material (arrows) that accumulates beneath the cuticle. Scale bars: (A, B, E, F) = 20 µm; (C, D) = 100 µm. Abbreviations: e = epidermis; I = idioblast; IP = intravacuolar precipitate; L = lipid body; M = mesophyll; N = nucleus; R = raphide; S = stalk of osmophore; Se = secretory layer; Sv = secretory vesicles; V = vacuole; Vb = vascular bundle.