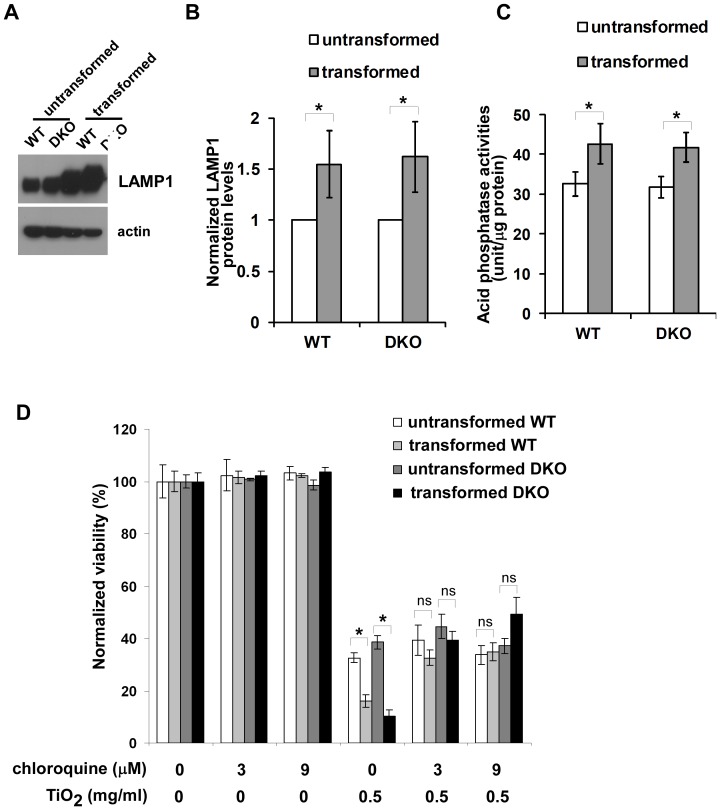
Figure 6. Selective cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles is related to an oncogenic transformation-induced increase of lysosomal activities.
(A) The expression levels of lysosomal protein LAMP1 in the indicated cells were determined by western blot. (B) The expression levels of LAMP1 are higher in transformed cells than their untransformed counterparts. The intensities of LAMP1 and actin shown in (A) were quantified using ImageJ software (NIH). The relative LAMP1 levels were calculated with the intensity of LMAP1 normalized to that of actin in the same sample. Data represent mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. * p<0.05, Student’s unpaired t test. (C) The enzymatic activities of lysosomal acid phosphatase were measured. Mean±S.D. of three independent experiments are shown. “*” indicates P<0.05, Student’s unpaired t test. (D) Chloroquine alleviates death of transformed cells induced by TiO2 nanoparticles. The indicated cells were cultured in the absence or presence of chloroquine or TiO2 nanoparticles. Cell viability was measured 24 hour after the treatments using TOTO-3 DNA dye exclusion approach. Data represent mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. “*” indicates P<0.05; “ns” indicates no significance (P>0.05), Student’s unpaired t test. The viabilities of TiO2 nanoparticle-treated transformed cell lines in the presence of chloroquine are significantly higher than those in the absence of chloroquine (p<0.05, Student’s unpaired t test), whereas the differences in the viabilities of untransformed cells with and without chloroquine exposure are not statistically significant (Student’s unpaired t test).