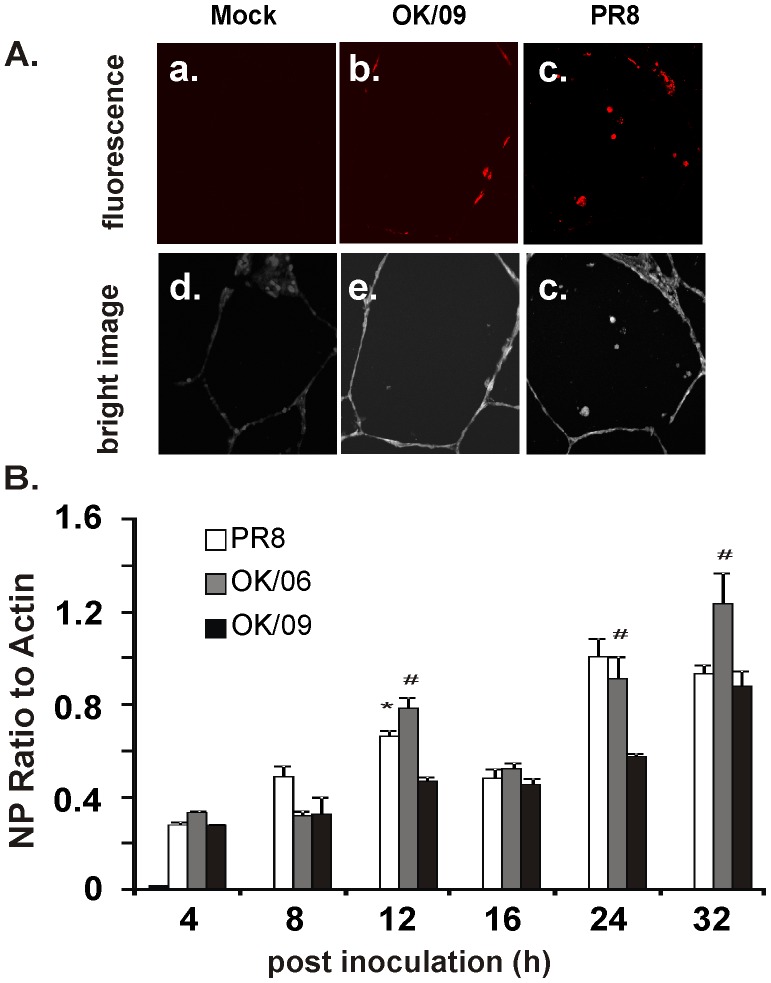
Figure 1. Exposure of human lung to both pandemic and prototypic influenza virus results in viral infection and replication in alveolar cells.
(A) The lung slices were processed for immunohistochemistry for detection of viral NP using rabbit polyclonal antibody (red). Panels a, b and c show mock (virus dilution buffer), OK/09 and PR8 infection, respectively. Panels d, e and f are corresponding bright-field images that demonstrate that lung architecture is preserved during the experiment. (B) Replication of influenza virus OK/09, OK/06 and PR8 in the human lung organ culture model. Lung slices exposed to virus at 6×106 PFU/ml were cultured for various times and total cellular mRNA was extracted. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed using Oligo dT as the primer for the first strand synthesis. Primers specific for NP were used to examine NP mRNA expression.