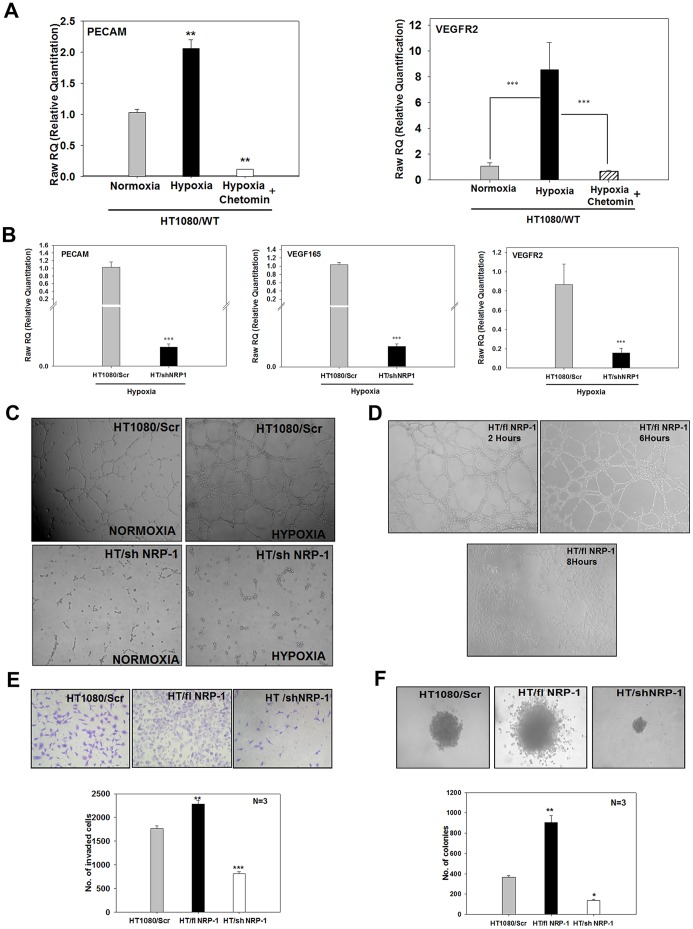
Figure 6. NRP-1 controls the hypoxia-induced angiogenic program in HT1080 cells. A.
Expression of PECAM and VEGFR-2 mRNA was quantified by performing real time PCR experiments on the HT1080/WT cells that were incubated under normoxia and hypoxia – with or without chetomin. Both PECAM and VEGFR-2 mRNAs were up-regulated by hypoxia. Presence of chetomin abrogated the up-regulation of PECAM and VEGFR2 genes by hypoxia indicating that these genes are regulated by the HIF-1α-mediated transcription. B. Quantitative PCR experiments performed on the HT1080/Scr and HT/shNRP-1 cells incubated under hypoxia show that hypoxia failed to up-regulate the expression of PECAM, VEGF165 as well as VEGFR-2 in the HT/shNRP-1 cells, indicating that the hypoxia-induced angiogenic program in the HT1080 cells is controlled by NRP-1. C. Tubule formation on matrigel by HT1080/Scr and HT/shNRP-1 cells under normoxia and hypoxia is depicted. The HT/shNRP-1 cells failed to form tubules even after priming with hypoxia (lower right hand panel), indicating that NRP-1 expression in critical for the enhanced tubule formation by the hypoxia-primed HT1080 cells. The hypoxia-primed wild type cells formed robust tubules as seen in the earlier experiments (upper right hand panel). D. HT/flNRP-1 cells form dense tubules even without the hypoxia-priming. The tubule formation by these cells started very early (2 hours) and became very dense by 6 hours (upper right hand panel). After 6 hours, the tubules collapsed as the HT/flNRP-1 cells invaded the matrigel vigorously (lower panel) forming a monolayer in the well. NRP-1 controls the tumorigenic properties of HT1080 cells. E. Matrigel-invasion property of HT1080/Scr cells was compared with that of HT/flNRP-1 and HT/shNRP-1 cells. A representative image of the invaded cells stained with crystal violet is depicted (Original magnification: 100X). Quantification of the invaded cells showed that the HT/flNRP-1 cells possessed significantly enhanced invasive property (N = 3; ** p<0.01) while the HT/shNRP-1 cells showed a significantly reduced invasive ability (N = 3; ***p<0.001). F. Anchorage-independent growth of HT1080/Scr, HT/shNRP-1 and HT/flNRP-1 was examined by performing soft agar colony assay. A representative phase contrast image of the colonies formed by these cells is illustrated (original magnification: 100X). The HT/flNRP-1 cells formed large colonies having loose migrating cells at the border (middle panel), while the HT/shNRP-1 cells formed very small compact colonies. Quantification of the colony formation shows that the number of colonies formed by the HT/flNRP-1 cells was significantly higher (**p<0.01) while that by the HT/shNRP-1 cells was significantly lower (* p<0.05) compared to the HT1080/Scr cells. Data show that NRP-1 expression is necessary for the anchorage-independent growth of HT1080 cells. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.M.