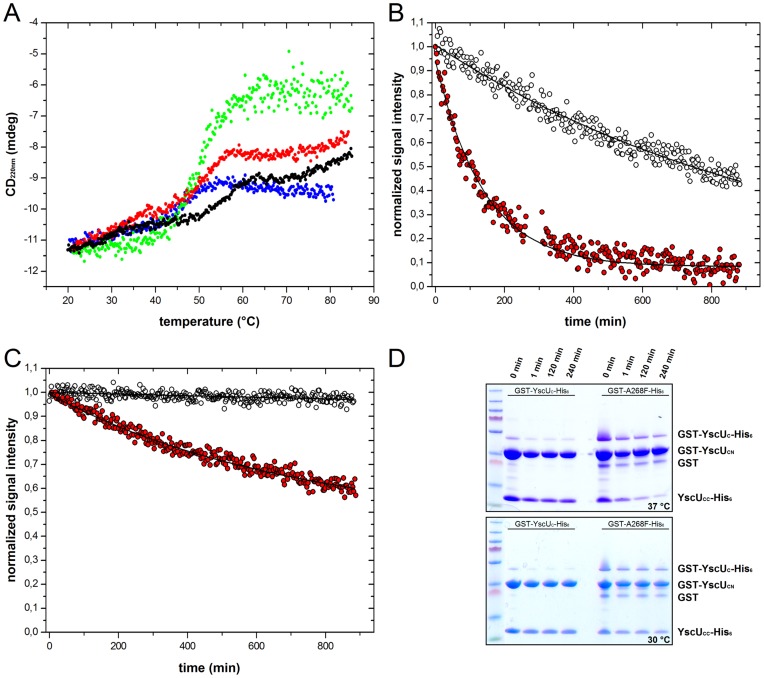
Figure 7. YscUC suppressor mutant stabilities and dissociation kinetics.
(A) Thermal induced unfolding of YscUC and suppressor mutants. Dissociation temperatures (T diss) of single suppressor mutants at pH 7.4 were quantified with the CD signal at 220 nm and a scan rate of 1°C/min; YscUC (black), A268F (blue), Y287G (green), and V292T (red). All suppressor mutants are destabilized compared to wild-type YscUC. T diss values are summarized in Table 3. (B), (C) Dissociation kinetics quantified as dissociation life-times (τdiss) of YscUC (black) and V292T (red) at pH 7.4 followed with NMR-spectroscopy at (B) 37°C and (C) 30°C, respectively. Primary NMR data for (B) is shown in Figure S6. Solid lines correspond to fits of the experimental data to single exponential decays. (D) Time dependent GST-pulldown experiments show the dissociation of wild-type YscUC and the suppressor mutant A268F at 30°C and 37°C after varying incubation times. The suppressor mutant A268F displayed pronounced dissociation of YscUCC-His6 at 37°C and moderate dissociation at 30°C; wild-type YscUC displayed no dissociation of YscUCC-His6 at 37°C or at 30°C over the observed time period. Note! Dissociation of YscUCC is manifested as disappearance of YscUCC-His6 over time since the dissociation is irreversible and YscUCC-His6 cannot bind itself to the used resin.