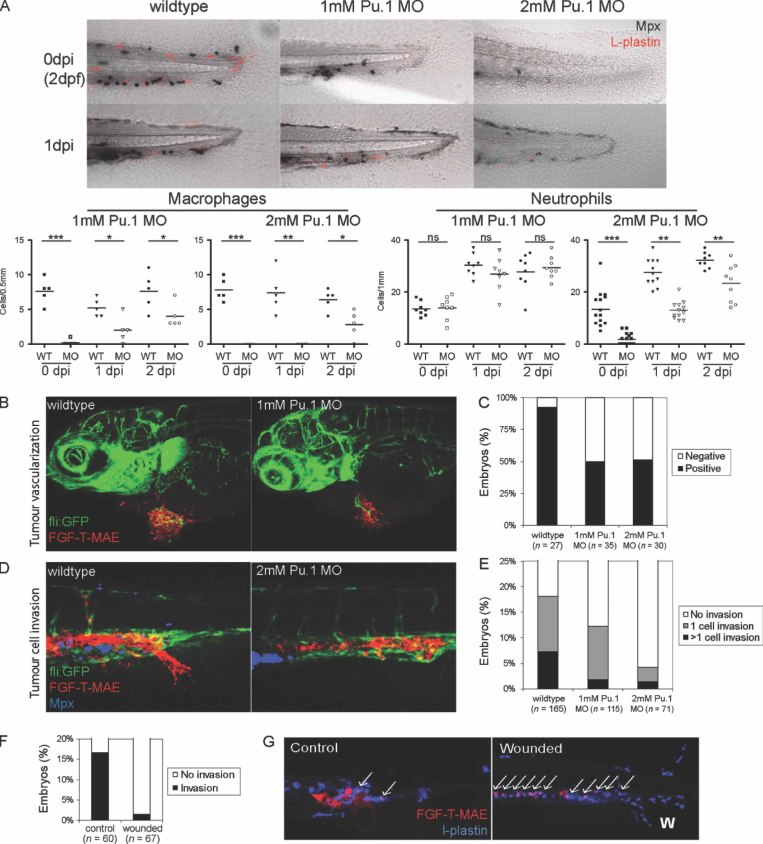
Figure 5.
Myeloid cells contribute to tumour vascularization and invasion. (A) Lineage-specific depletion of macrophages and neutrophils by dose-dependent morpholino-mediated knockdown of Pu.1. Neutrophils are shown in black (Mpx+ histochemical staining) and macrophages are shown in red (Mpx−/L-plastin+). In each embryo, the macrophages in the region 0.5 mm from the posterior end of the tail fin and the neutrophils in the region 1 mm from the posterior end of the tail fin were quantified, which are sufficient to represent each linage distribution in the entire embryo. (B, C) Suppression of FGF-T-MAE tumour vascularization under partial (1 mm) or complete (2 mm) knockdown of Pu.1 was significant (Wilcoxon test, p < 0.01). Representative embryos with tumour vascularization in the control and Pu.1 knockdown conditions at 3dpi are shown in (B) and quantification of tumour vascularization at 1dpi are shown in (C). Data are representative of > three independent experiments (each n ≥ 27). (D, E) Suppression of FGF-T-MAE tumour cell invasion at the posterior end of the CHT under complete knockdown of Pu.1 was significant (Wilcoxon test, p < 0.01). Representative control and Pu.1 knockdown embryos at 1dpi (D) and embryos scored for tumour cell invasion at 1dpi (E). Data are representative of > three independent experiments (each n > 70). (F) Suppression of tumour cell invasion by wound inflammation in the tail fin at 1dpi was significant (Wilcoxon test, p < 0.001). A wound in the tail fin was made mechanically (as in Figure 7D) just after implantation of tumour cells at 2dpf. Data are representative of three independent experiments (each n ≥ 60). (G) Phagocytosis of tumour cells (indicated by arrows) around the invasion site by myeloid cells in embryos in which the tail fin was wounded (positioned by ‘W’); tumour cells are shown in red and myeloid cells were stained for L-plastin (blue). Images are representative of > three independent experiments (each n > 30). Images in (A, B, D) were acquired using a Leica TCS SPE confocal microscope with a × 20 dry objective; those in (G) were acquired using a Zeiss LSM exciter on an Axio Observer confocal microscope with a × 20 dry objective