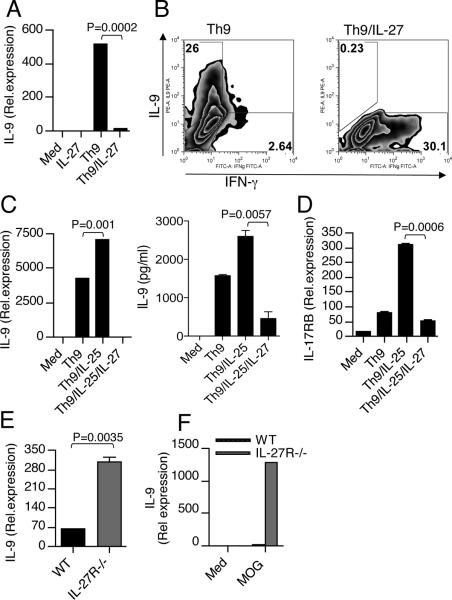
Figure 3. IL-27 inhibits Th9 differentiation both in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Real-time PCR and (B) flow cytometry analysis of naïve CD4+ T cells activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 under Th9-inducing conditions in the presence or absence of IL-27. Results are representative of five independent experiments. (C) Real-time PCR and ELISA of IL-9 in naïve CD4+ T cells cultured under Th9 conditions together with IL-25 in the presence or absence of IL-27. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of IL-25R on Th9 cells stimulated with or without IL-27. (E) Real-time PCR for IL-9 mRNA in CD4+ T cells isolated from the CNS of WT and IL-27R−/− mice with EAE. (F) Splenocytes from WT and IL-27R−/− mice were harvested 10 d after immunization and were stimulated ex vivo with MOG peptide 35–55. IL-9 levels were measured by real-time PCR. Results are representative of three independent experiments.