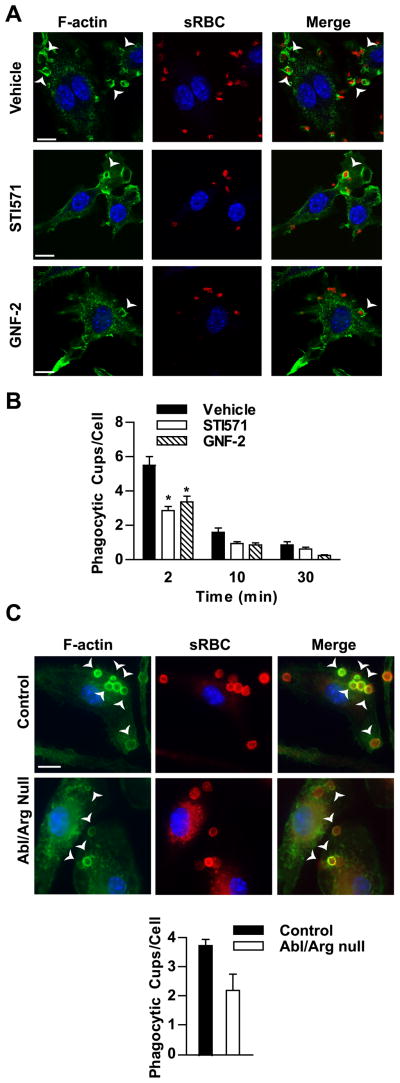
Figure 4. Abl family kinase activity is required for efficient phagocytic cup formation.
(A) RAW264.7 pretreated with either STI571 (10 μM) or GNF-2 (20 μM) were incubated with rabbit-IgG opsonized sRBCs for 2 minutes. Cells were then fixed and stained for F-actin (green) and Hoechst to mark nuclei (blue). IgG-opsonized RBCs were stained with PE-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies. Phagocytic cups were imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) RAW264.7 cells treated with inhibitors were stimulated with IgG-opsonized sRBCs for the indicated times and processed as in (A). The number of phagocytic cups present in 100 randomly selected cells was counted. Results are representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 versus vehicle-treated cells. (C) BMDM from control and Abl/Arg null mice were stimulated with IgG-opsonized sRBCs for 5 minutes and processed as in (A). The numbers of phagocytic cups in control and Abl/Arg null cells were quantified as in (B). Results from two sets of control and Abl/Arg null BMDM are quantified. Scale bar = 10 μm. Arrows point to F-actin rich cups.