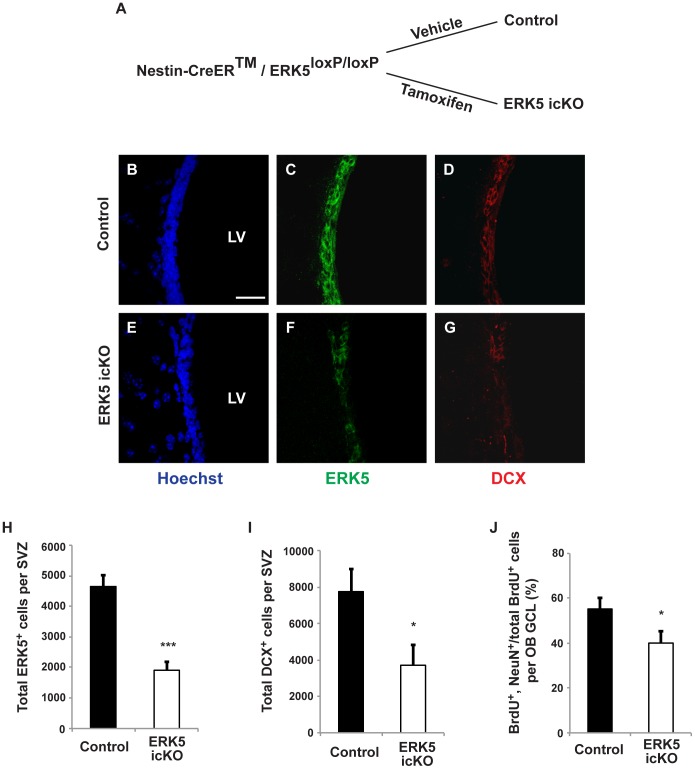
Figure 2. Inducible and conditional knock out of erk5 significantly reduces ERK5 protein expression along the SVZ, the number of DCX+ cells in the SVZ, and the number of adult-born neurons in the OB.
A) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. B–G) Representative immunostaining photomicrographs of ERK5 (green) and DCX (red) in vehicle control-treated mice (B–D) as well as tamoxifen-treated ERK5 icKO mice (E–G). Scale bar in B represents 25 µm and applies to C–G. H) Quantification of total ERK5+ cells along the SVZ. I) Quantification of total DCX+ cells along the SVZ. J) The deletion of erk5 decreases the total number of adult-born neurons (BrdU and NeuN double-positive cells among total BrdU+ population) in the granule cell layer of the OB 3 weeks after BrdU injection. n = 5 individual mouse brains and olfactory bulbs per treatment condition.