Fig. 2.
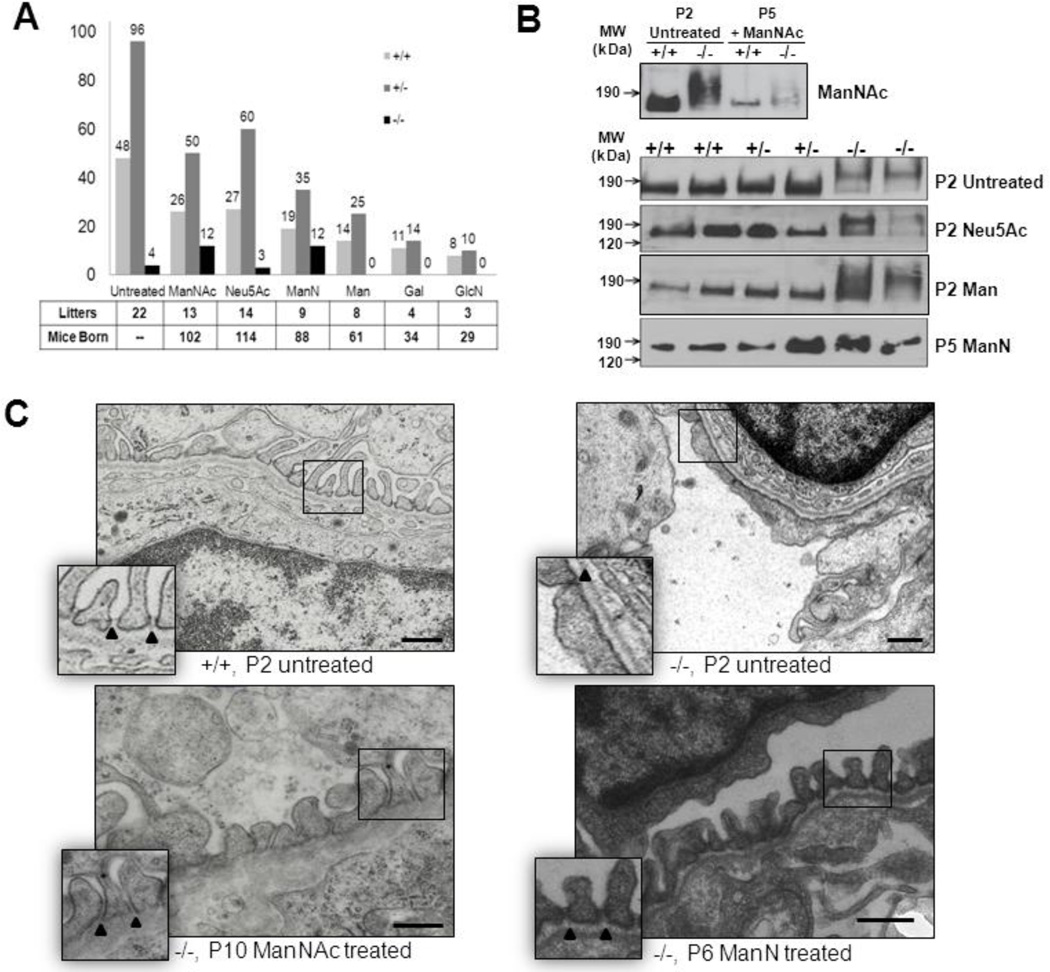
Assessment of the effects of oral monosaccharide administration on neonatal survival rate, kidney podocalyxin sialylation and renal ultrastructure in the Gne p.M712T mouse model. +/+ wild type Gne+/+; +/−, heterozygous Gne+/M712T; −/−, mutant GneM712T/M712T. Scale bars: 0.5 µm.
(A) Survival rates at P5 (past the critical age of P3) of litters born to heterozygous breeding pairs that were either untreated or treated with one of several monosaccharides (1 g/kg/day) in their drinking water. Total numbers of counted litters and mice born per treatment group are indicated. Note that the survival rate of mutant (−/−) pups significantly increased upon ManNAc (~47% survival rate) and ManN (~55% survival rate) therapy compared to the untreated group (~ 8%). Neu5Ac, Man, Gal, and GlcN therapy to pregnant and nursing mice did not improve survival rate of their mutant pups beyond P3.
(B) Immunoblots of kidney extracts (ages P2 or P5) labeled with antibodies against podocalyxin (~150 kDa). Wild-type (+/+) and heterozygote (+/−) specimens show normal migration, while slower podocalyxin migration (~190 kDa) occurs in untreated, Neu5Ac and Man treated mutant pups (P2), indicating hyposialylation. Podocalyxin migration in ManNAc and ManN treated mutant pups (P5) is within the range of wild type and heterozygous kidney extracts, indicating a rescued sialylation status.
(C) Representative electron microscopy images of juxtamedullary glomeruli in kidney sections of wild type (+/+, P2), mutant (−/−, P2), ManNAc (−/−, P10) or ManN treated (−/−, P6) pups. Wild type glomeruli contain interdigitating foot processes with open slit junctions (arrowheads), an intact glomerular basement membrane and fenestrated endothelial cells. Glomeruli of untreated mutant pups show effaced foot processes with occluding junctions (arrowhead), segmental splitting of the basement membrane and seemingly normally fenestrated endothelial cells. In ManNAc- or ManN-supplemented mutant pups, the podocyte effacement is reduced and basement membrane integrity is partially restored with mostly intact podocyte slit junctions.