Figure 4.
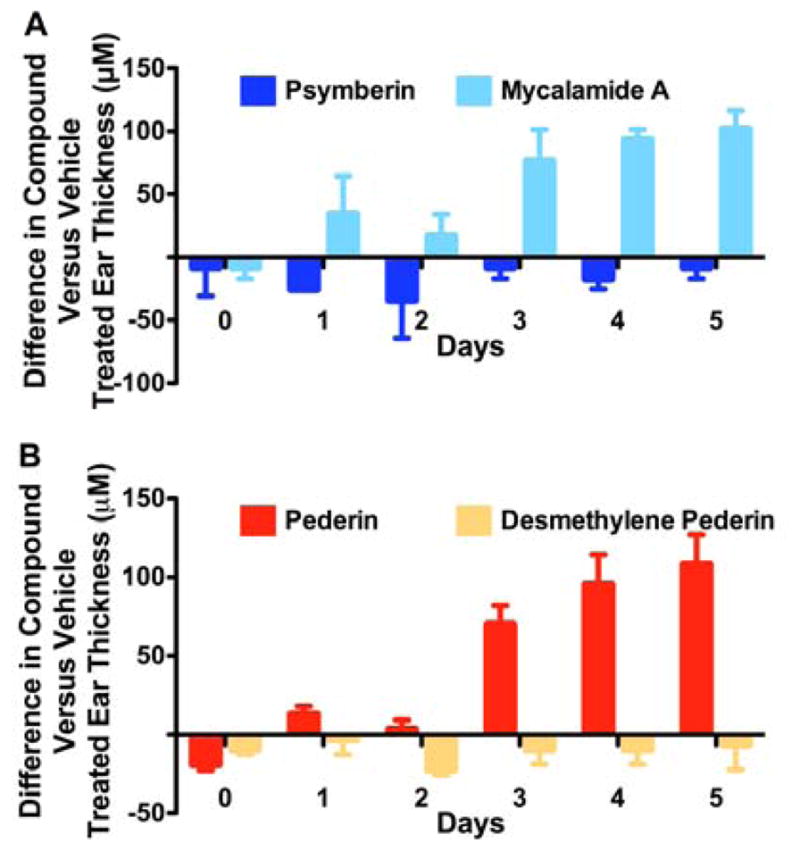
The vesicant activity of pederin, mycalamide, and psymberin differ. The abdomen of C57BL/6 mice was shaved using an electrical razor and 100 ml of vehicle solution (5% ethanol in 3:1 acetone:olive oil) was applied. Seven days later, 25 ml of a 0.00125% w/v solution of psymberin or mycalamide A. (A) or pederin or its synthetic analog, demethylene pederin (B) prepared in the same vehicle were applied to either the right or left ear of the treated mice. The opposing ear was treated with vehicle only. Prior to the ear application and then each day thereafter for 5 days, the thickness of both ears was measured by an investigator blinded to the treatment using a modified Mitutoyo micrometer. The differences in ear thickness between compound and vehicle treated ears in mm are plotted.
