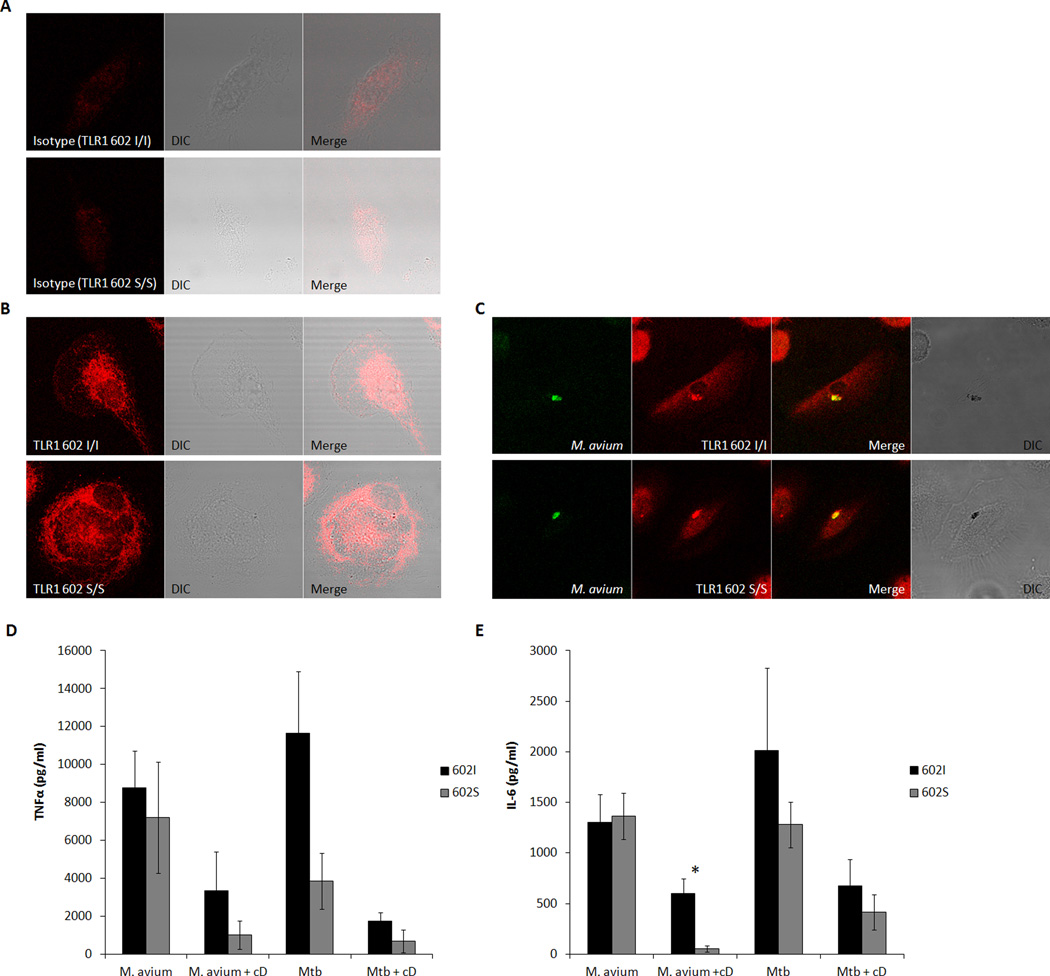
Figure 2. Intracellular TLR1 602S gains access to phagocytized mycobacteria in endosomal compartments.
A. Isotype control staining (red) of permeabilized resting macrophages from a TLR1 602I/I (top) or TLR1 602S/S (bottom) blood donor. B. Total TLR1 staining (red) of permeabilized resting macrophages from a TLR1 602I/I (top) or TLR1 602S/S (bottom) blood donor. C. Monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated with auramine-O labeled M. avium (green) for 15 minutes. Cells were subsequently fixed, permeabilized, and stained for TLR1 (red). Primary human monocyte-derived macrophages from venous blood donors of the indicated TLR1 602 genotypes were stimulated for 12 hrs with Mycobacterium avium or Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the presence or absence of cytochalasin D (cD), followed by ELISA quantification of secreted TNFα (D) or IL-6 (E). Error bars represent the standard deviation of at least three donors. Asterisks denote significant differences between TLR1 602I-expressing cells versus TLR1 602S/S cells (*p<0.05) (black bars; TLR1 602I/I or TLR1 602I/S donors, grey bars; TLR1 602S/S donors). (DIC; differential interference contrast, Mtb; Mycobacterium tuberculosis, cD; cytochalasin D