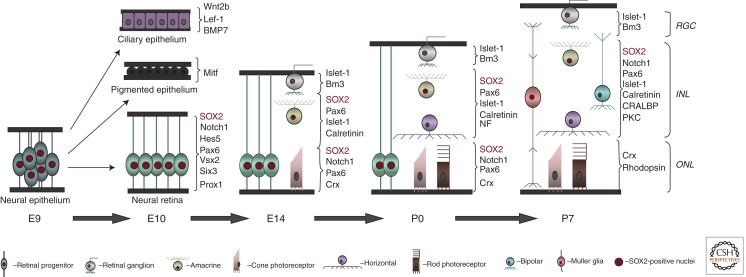
Figure 7.
Temporal progression of retinogenesis in the mouse. During development of the optic cup, neural epithelium of the optic vesicle gives rise to pigmented and ciliary epithelia, as well as neural retinal progenitor cells. The embryonic wave of neurogenesis in the retina is characterized by production of early-born retinal ganglion cells, horizontal interneurons, cone photoreceptors, and amacrine interneurons. Postnatal retinal progenitor cells predominantly give rise to rod photoreceptors, bipolar interneurons, and Müller glia. In the adult neural retina, neuronal and glial cell types are organized into three distinct cellular layers. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer.