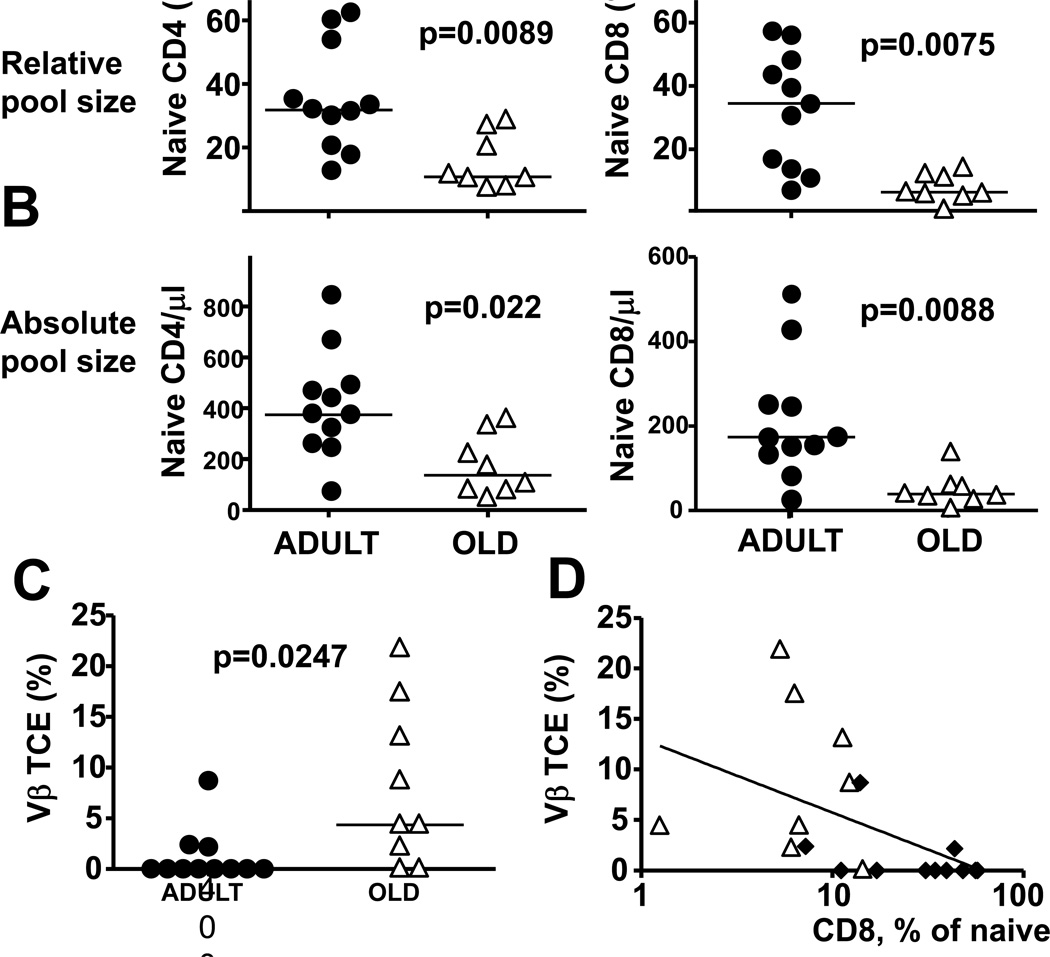
Fig. 3. Age-related differences in CD8 naïve pool size and stable TCE occurrence correlate inversely.
(A, B). Three weeks before vaccination, blood lymphocytes were analyzed by FCM for the frequency and absolute count of naïve CD4 and CD8 T-cells Naive CD4 T-cells (left panels), and naïve CD8 T-cells (right panels) defined by restrictive progressive gating (via CD4 or CD8 , then through the CD28hiCD95lo gate) were quantified in individual monkeys in terms of their frequency with CD4 or CD8 pools (A), or in terms of their number per ml of blood (B). Symbols indicate the naïve T-cell percentage in individual old or adult monkeys, horizontal lines show means. p-values reflect Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test results. (C) cDNA from blood lymphocytes was analyzed yearly by PCR for TCR length polymorphism in each of the 24 V regions of the β TCR chain for 4 consecutive years, and Vβ families exhibiting consistently a single PCR band for at least the last two time points were defined as TCE+. Symbols indicate percentages of TCE+ Vβ families in individual monkeys, horizontal lines show means. (D) Naïve cell frequencies (x-axis) were correlated to the percentage of TCE+ Vβ families (y-axis) in individual adult (black diamonds) or old (white triangles) monkeys. A semilogarithmic correlation index for combined groups is indicated.