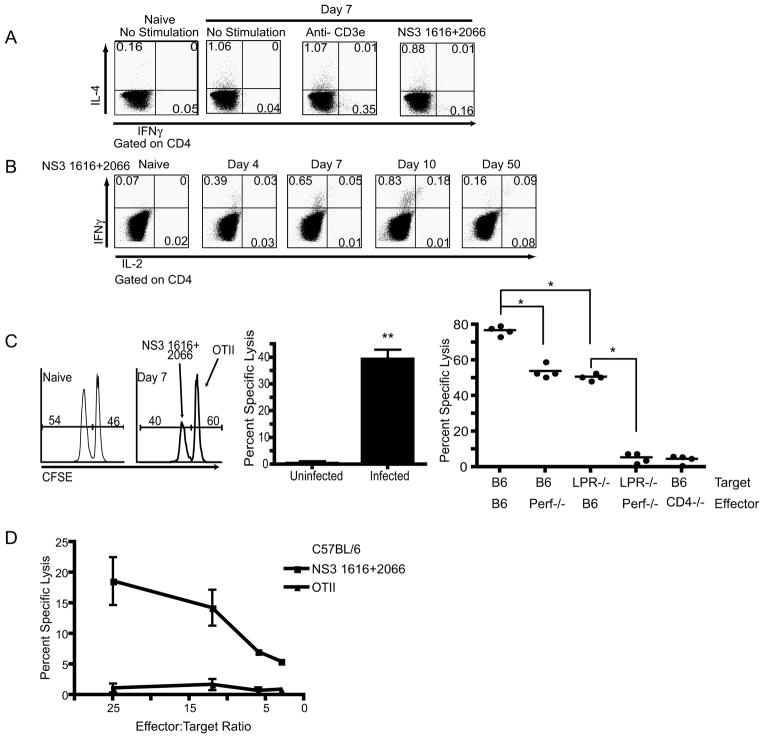
Figure 4. Functional potential of antigen specific CD4 T cells.
A. Representative example of a CD4 T cell cytokine response 7 days post infection. Following gating on CD4, IFNγ and IL-4 were measured after 6 hr stimulation in the presence of monensin. Cells were stimulated with media, 2c11 (0.5μg/ml) or NS31616+2066(10−6M), and a naïve mouse was used as a control. One mouse of four is shown, from one representative experiment of two. B. Representative example of CD4 T cell ICCS during the course of infection, as indicated above each plot. Following gating on CD4, IFNγ and IL-2 were measured after 6 hr stimulation with NS31616+2066(10−6M) in BFA. Controls and repetitions were as in A. C. In vivo CD4 T cell CFSE cytotoxicity assay. Left panel- Representative histogram of transferred (donor, Ly-5.1+) splenocytes 12 hours after adoptive transfer of target cells into naïve (left histogram) and infected (right histogram) mice. Middle panel- Aggregate quantification of in vivo CD4 T cell CFSE based cytotoxicity assay. CD4 T cells were cytolytic in vivo on day 7 post WNV infection (**p<0.008). Results represent the average of 5 mice per group, and are representative of three independent experiments. Right panel- Quantification of in vivo CD4 T cell CFSE-based cytotoxicity assay completed within WNV infected Perforin−/−, CD4−/− and B6 control mice. B6 or LPR−/− splenocytes were coated with WNV or control peptides, labeled with CFSE and used as targets with different hosts – the x-axis legend denotes which molecule(s) were missing during the interaction of CTL with their targets. B6 (targets) transferred into Perf−/− mice as well as the transfer of LPR−/− deficient targets leads to a reduction in cytotoxicity (*p<0.03). Transfer of LPR−/− targets into perf−/− mice leads to a complete ablation of cytotoxicity (p<0.03). Results represent the compilation 2 independent experiments. D. In vitro CTL activity of purified CD4 T-cells against targets coated with indicated WNV peptides or the control class II-restricted ovalbumin peptide (OT-II, Ova323-339). IC21 cells were coated with the indicated peptides and labeled with 51Cr. The cells were incubated with CD4 T-cells purified from spleens of B6 mice infected with WNV 7 days earlier, as described, with minimal purity of 89% and contaminating CD8 or B-cells at <0.5%. Chromium release assay was performed as described in Methods. Results are representative of 3 experiments.