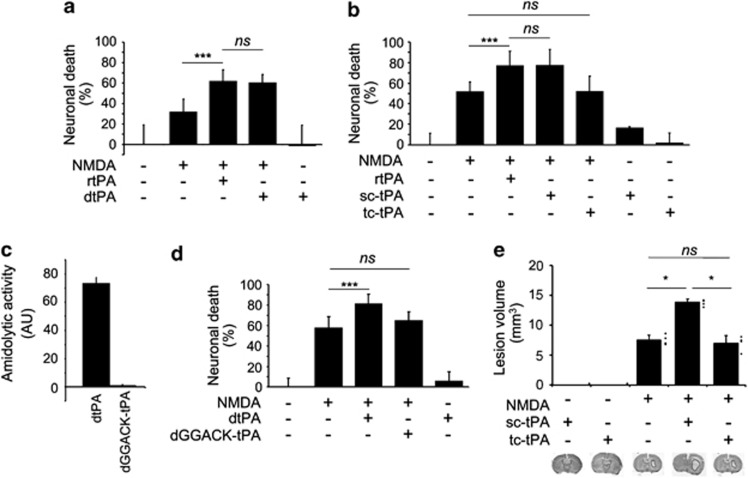
Figure 4.
Whereas sc-tPA promotes NMDAR-mediated neurotoxicity through its proteolytic activity, tc-tPA does not. (a, b and d) Neuronal death was assessed by measuring LDH release in the bathing media 24 h after a 1 h exposure of primary cultured cortical neurons (14 DIV) to 50 μM NMDA alone or supplemented with either (a) rtPA or dtPA (0.3 μM; n=12, four independent experiments), (b) rtPA, sc-tPA or tc-tPA at 0.3 μM (n=16, four independent experiments), or (d) rtPA, dGGACK-tPA at 0.3 μM (n=12, three independent experiments). Data are presented as the mean value±S.D. of neuronal death in percent relative to control. (c) Incubation of dtPA with the chloromethylketone dGGACK produced an inactive form of sc-tPA as assayed by fluorogenic assay (dGGACK-tPA). (e) NMDA-induced excitotoxic brain lesions measured (thionine staining) 24 h after intrastriatal injections of NMDA (10 mM) either alone or in the presence of either sc-tPA or tc-tPA (45 μM, n=4). Data are presented as the mean values±S.D. of lesion volumes in mm3 (***P<0.01; *P<0.05; ns: not significant)