FIGURE 8.
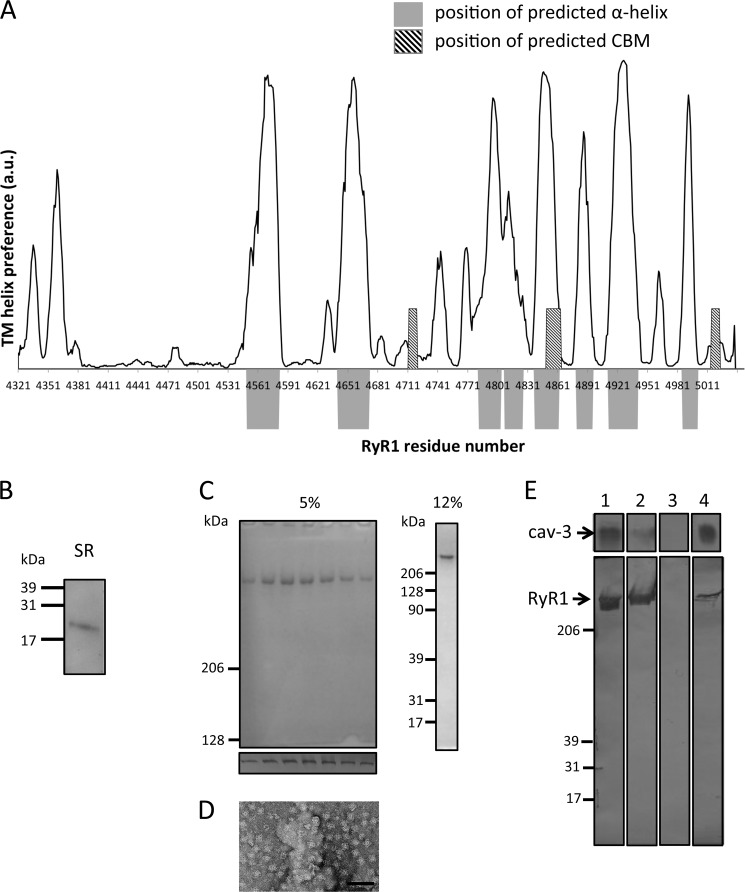
Nonameric cav-3 binds purified RyR1 homotetramers. A, regions predicted to form transmembrane α-helices and the location of CBMs are displayed (data analyzed using SPLIT tool). The regions that are predicted to form TM α-helices are indicated by the position of the solid gray blocks. Superimposed are the locations of the CBMs, hatched box. The plot shows that two of the CBMs (Table 1, CBMs 2 and 6) are located at regions that are not predicted to be hydrophobic or form α-helical structures. B, Western blotting of JTC SR membrane proteins separated by SDS-PAGE identifying cav-3 as a constituent. C, Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE (5%) illustrating the purity of RyR1 with Western blotting of each fraction (lower panel) confirming the identity of the isolated protein as RyR1. The 12% SDS-PAGE shows no accessory proteins have co-purified with RyR1. D, TEM image of a field of purified RyR1 complexes shows that it has been purified as a homotetramer. E, Western blot of cav-3 and RyR1 showing an interaction. Lane 1, loaded protein cav-3, top; RyR1, bottom. Lane 2, unbound protein. It can be seen that the majority of cav-3 bound to the resin and that a portion of RyR1 did not bind to the immobilized cav-3. Lane 3 shows that after multiple washing steps there was no nonspecifically bound protein present. Lane 4, both cav-3 and RyR1 were detected in the eluent indicative of RyR1 having bound to cav-3.