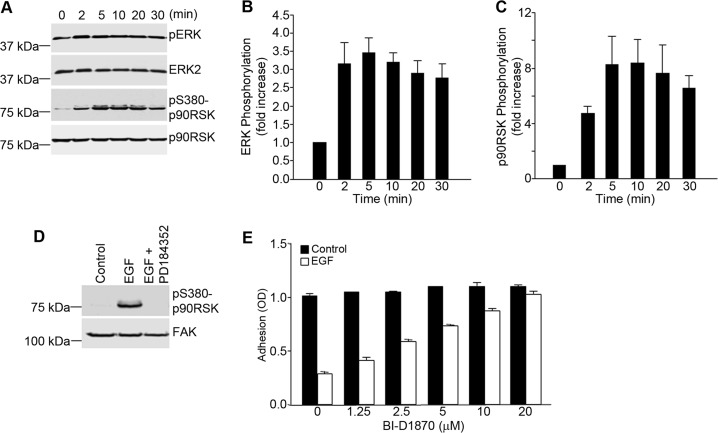
FIGURE 4.
EGF-dependent inhibition of α5β1 integrin function in A431 cells requires the MEK/ERK/p90RSK pathway. A, A431 cells were seeded onto poly-l-lysine-coated wells and stimulated with EGF (3 nm) for the indicated times. Nuclear free cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting for the phosphorylation of ERK and p90RSK. Staining for total ERK and total p90RSK served as loading controls. pS380-p90RSK, phospho-Ser-380 p90RSK. B and C, the bands shown in A were quantified and normalized to ERK2 (B) and p90RSK (C), respectively. Densitometry measurements were performed using ImageJ software. Values are means ± S.D. of three separate experiments. D, A431 cells were seeded onto poly-l-lysine-coated wells, pretreated with PD184352 (2.5 μm), and incubated with EGF (3 nm) for 20 min. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to phosphorylated p90RSK. Staining for total FAK served as a loading control. E, A431 cell suspensions were pretreated for 1 h with an inhibitor of p90RSK (BI-D1870) at the indicated concentrations prior to cell adhesion to fibronectin-coated wells in the absence or presence of EGF (3 nm). Cell adhesion was assessed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Error bars indicate S.D. of triplicate samples for one of three representative experiments.