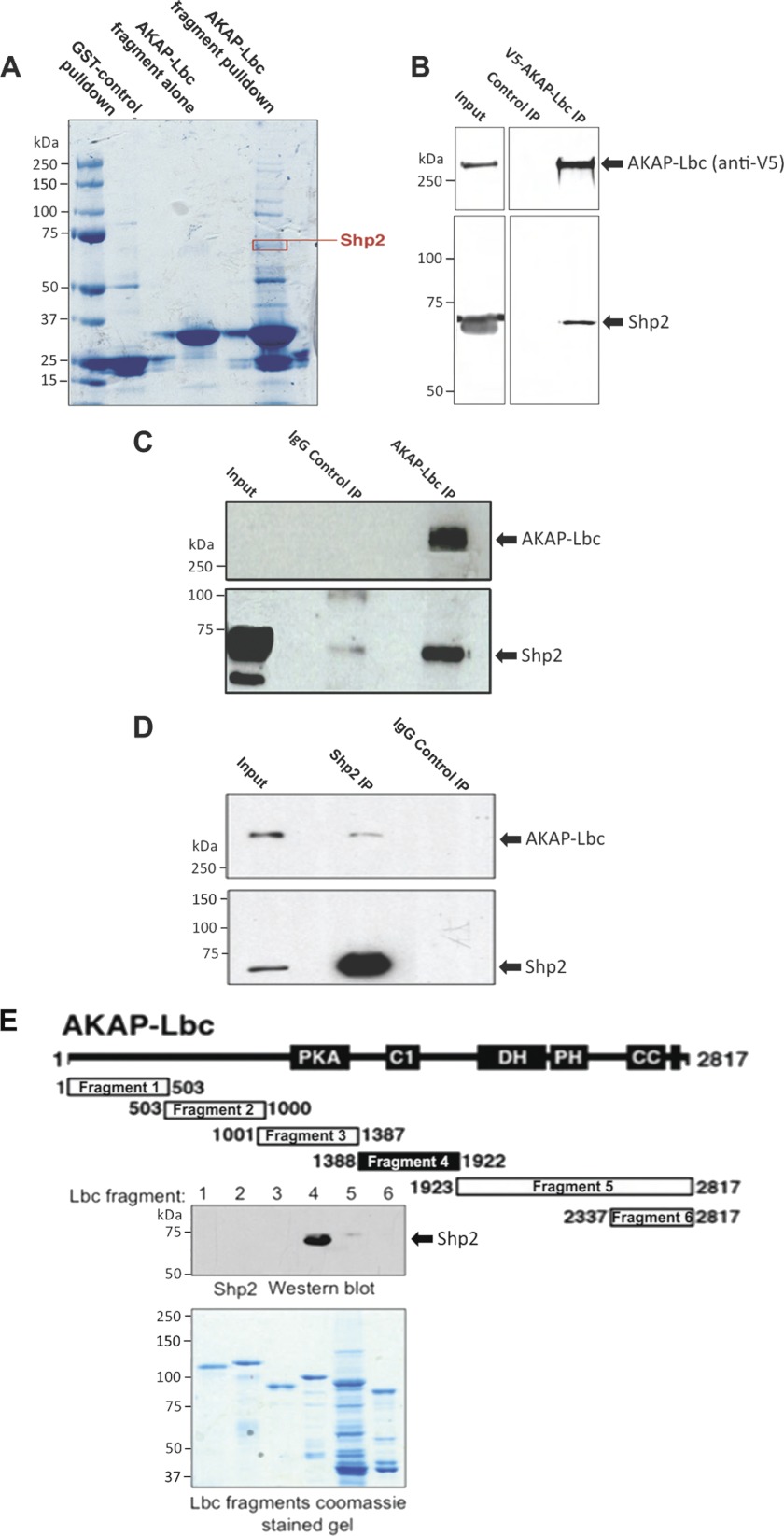
FIGURE 1.
Shp2 interacts with AKAP-Lbc. A, identification of Shp2 co-purifying with AKAP-Lbc by mass spectrometry. Heart extract was used for GST-AKAP-Lbc fragment (amino acid residues 1756–1801) pulldowns (2 mg of heart extract per pulldown). The resulting material was eluted from the GST-agarose and concentrated. Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining and identified by tandem MS. B, co-IP of endogenous Shp2 with V5-AKAP-Lbc. HEK293 cells were transfected for expression of V5-tagged AKAP-Lbc. AKAP-Lbc was immunoprecipitated with anti-V5-agarose from cell lysates. Parallel control IPs were performed using an equal amount of lysate where V5-AKAP-Lbc was not expressed (Control IP). IPs were washed, and the bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Detection of Shp2 and AKAP-Lbc was carried out by immunoblotting. C, co-IP of endogenous Shp2 with endogenous AKAP-Lbc in heart. AKAP-Lbc was immunoprecipitated from mouse heart extract (5 mg of total protein). Parallel control IgG IPs were carried out using an equal amount of heart extract. IPs were washed, and the bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose. Detection of AKAP-Lbc and co-purifying Shp2 were carried out by immunoblotting. D, co-IP of endogenous AKAP-Lbc with endogenous Shp2 in heart. Shp2 was immunoprecipitated from mouse heart extract, and detection of AKAP-Lbc and co-purifying Shp2 were carried out by immunoblotting (as described for C). E, mapping of Shp2 binding to AKAP-Lbc indicating that Shp2 binds to amino acid residues 1388–1922 of AKAP-Lbc. Diagram shows GST-AKAP-Lbc fragments used for pulldown experiments. Shaded area indicates Shp2 binding fragment as determined by immunoblot detection of Shp2 co-purifying with AKAP-Lbc fragments by GST pulldown from heart extract. Coomassie-stained gel indicates equal expression of the AKAP-Lbc fragments that were used for GST pulldown.