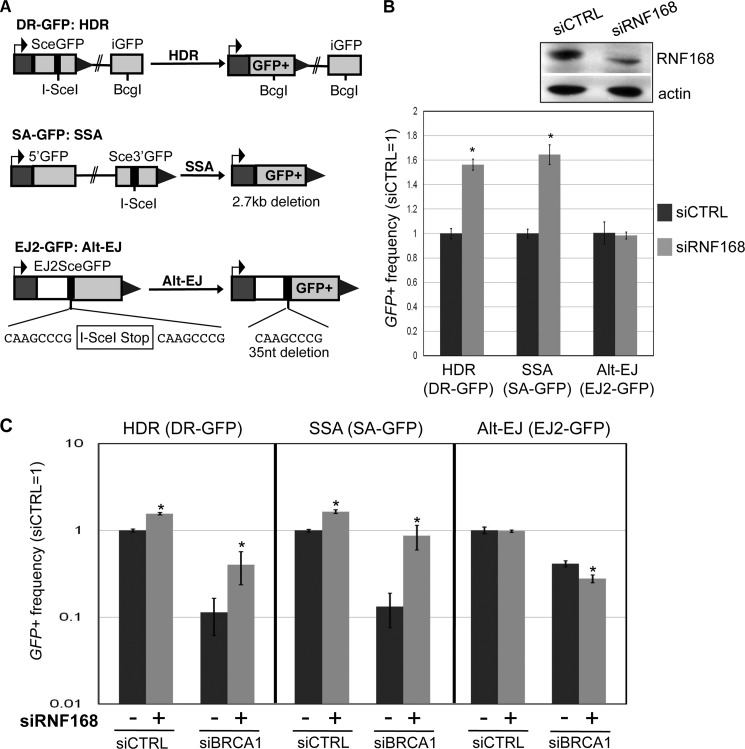
FIGURE 1.
RNF168 inhibits HDR and SSA, and depletion of RNF168 can suppress the defects in these HR events caused by BRCA1 silencing. A, shown are three reporters with an I-SceI recognition site, along with each respective DSB repair event that restores GFP+: HDR for DR-GFP, SSA for SA-GFP, and Alt-EJ for EJ2-GFP. B, depletion of RNF168 causes an increase in HDR and SSA, but not Alt-EJ. U2OS reporter cell lines were transfected with siRNF168 (pool of four siRNA sequences) prior to co-transfection of siRNF168 and an expression vector for I-SceI. Shown are the frequencies of GFP+ cells for each reporter cell line, relative to parallel transfections with a nontargeting siRNA (siCTRL). *, p < 0.0001 (n ≥ 3). Also shown are immunoblot signals for RNF168 and actin for siRNF168- and siCTRL-treated samples. C, depletion of RNF168 suppresses the HDR and SSA defects caused by BRCA1 silencing. U2OS reporter cell lines were treated with siCTRL or siBRCA1, along with (+) or without (−) siRNF168. For all (−) siRNF168 treatments, siCTRL was added to ensure equivalent concentrations of total siRNA. Repair was then analyzed as in B. Shown are the frequencies of GFP+ cells for the HDR, SSA, and Alt-EJ reporter cell lines for each siRNA treatment, relative to siCTRL. *, p < 0.0001 for HDR and SSA, p = 0.0025 for Alt-EJ, versus the (−) parallel siRNF168 condition (n ≥ 3).