FIGURE 5.
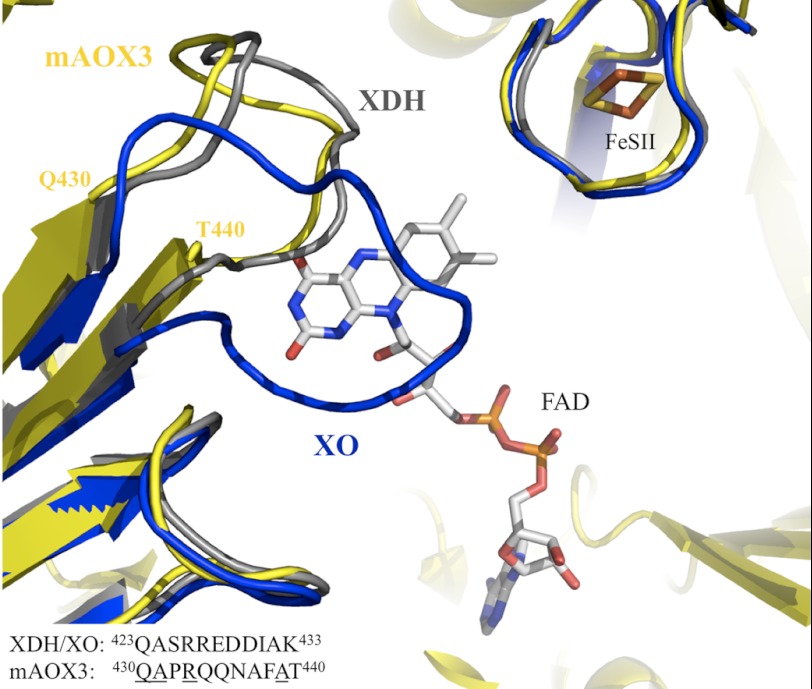
Superposition of mAOX3 (yellow), bXDH (gray), and bXO (blue) at the FAD binding site, viewed from the solvent. The FAD and the [2Fe-2S] II are represented color-coded and correspond to the mAOX3 structure. Note the change in the variable loop (residues Gln-423–Lys-433 in bovine XDH numbering) between XO and XDH forms. The FAD molecule occupies a vast area within the protein, with the isoalloxazine ring in close proximity to the solvent-accessible area, and pointing toward the FeSII center. The FAD cofactor is 9.0 Å away from the FeSII, whereas the distance from the exocyclic NH2 of the pterin to the nearest FeSI is 5.1 Å.