FIGURE 9.
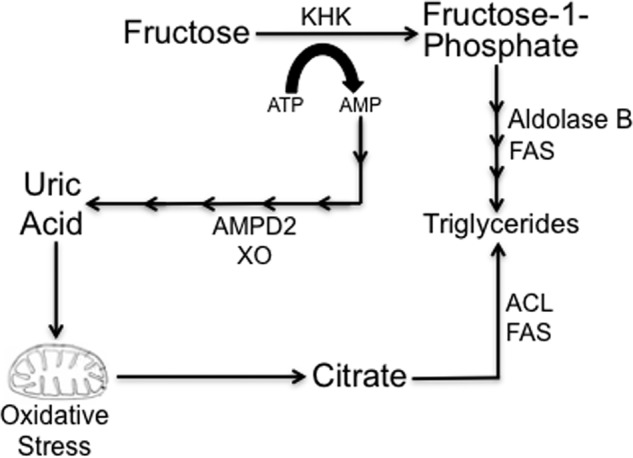
Potential mechanisms whereby uric acid mediates fat accumulation in hepatocytes. Uric acid is a by-product of fructose metabolism generated from the ATP depletion induced by KHK in fructose phosphorylation. AMP is converted to uric acid by the action of several enzymes, including AMP deaminase (AMPD2) and xanthine oxidase (XO). Direct fructose metabolism results in increased TG synthesis by AldoB and fatty-acid synthase (FAS). Similarly, uric acid induces mitochondrial oxidative stress and citrate release to the cytosol for de novo triglyceride synthesis from citrate and acetyl-CoA via ATP citrate lyase (ACL) and FAS.
