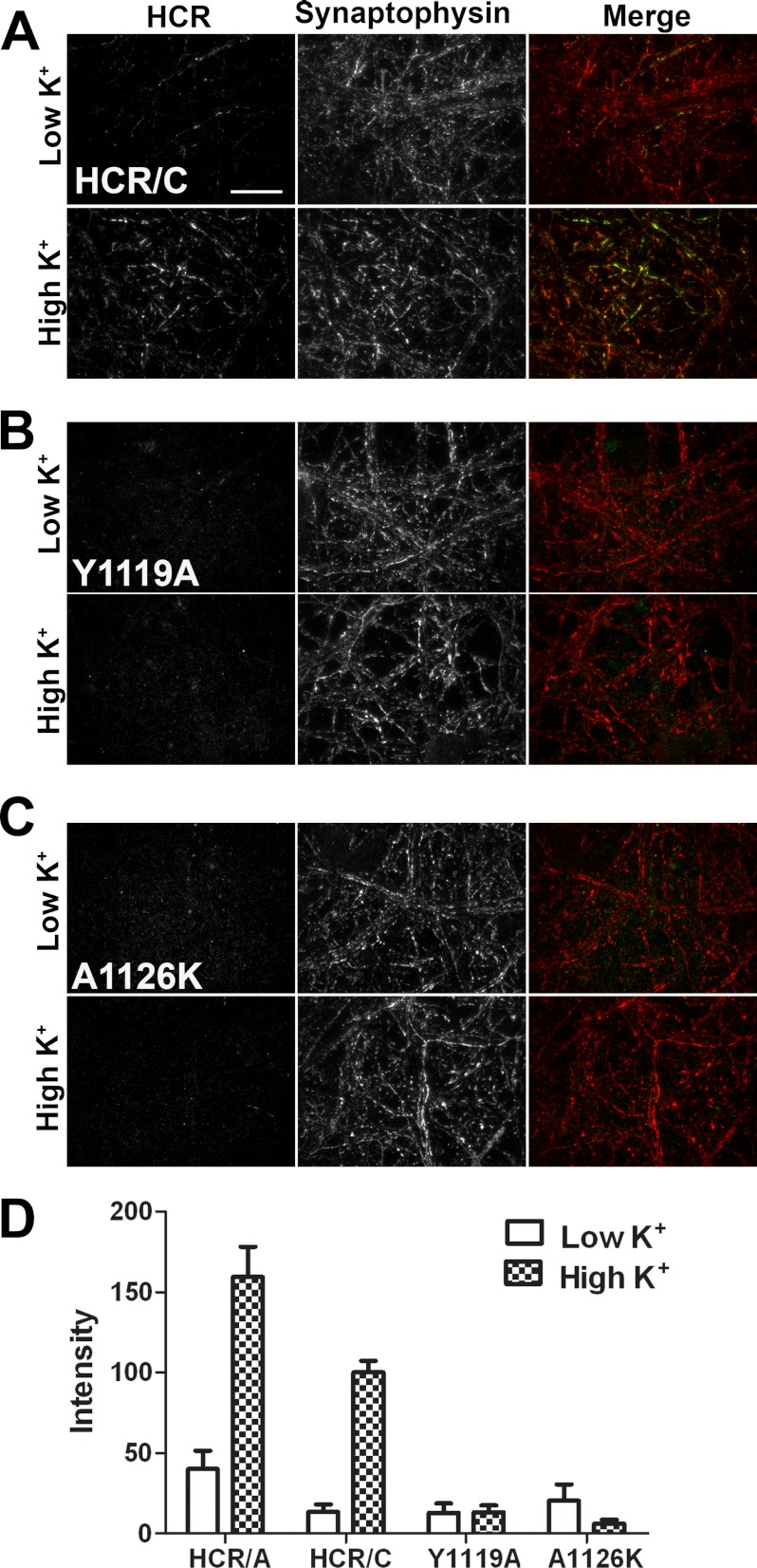
FIGURE 6.
Synaptic activity enhances the uptake of HCR/C. A, primary hippocampal neurons were incubated in the presence of HCR/A, HCR/C, or HCR/C derivatives (40 nm) for 5 min under resting (low K+) or depolarizing (high K+) conditions. The cells were processed for microscopy. Bound/internalized HCR was detected with an anti-HA antibody followed by a fluorescent secondary antibody. Synaptic vesicles were identified by staining for synaptophysin. Micrographs were captured using TIRF microscopy with identical exposure settings between treatments. Representative ×100 micrographs are shown. Scale bar = 20 μm. Images were adjusted to the same brightness and contrast using NIS Elements. Representative merged micrographs are shown for HCR/C (A), HCR/C(Y1119A) (B), and HCR/C(A1126K) (C). Under resting conditions, the cells appear red in the merged images, as only the synaptophysin signal is detected. Following depolarization, some of the neurons projections in the field appear yellow or green, indicating uptake of the HCR and overlap with synaptophysin. D, quantification of microscopy data. Eight random, synaptophysin-positive fields per treatment were captured with identical exposure settings between treatments. The HCR fluorescence, in arbitrary units, was measured using NIS Elements. The graph was prepared for presentation using GraphPad Prism. An average of four independent experiments is shown.