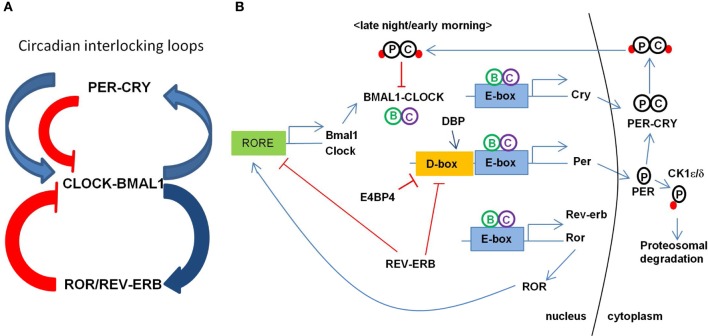
Figure 1.
Transcriptional regulation circuit of clock genes in mammals. (A) Circadian interlocking loops show that a primary loop of CLOCK-BMAL1 and PER-CRY complexes and an additional feedback loop of ROR/REV-ERB, conferring a tight transcriptional regulation. The blue arrows indicate the transcriptional activation and the red lines indicate the inhibiting activity of the targets. ROR as an activator and REV-ERB as a repressor regulate the expression of BMAL1. (B) Transcription of BMAL1 and CLOCK is regulated by ROR and REV-ERB through binding RORE elements at their promoters. CLOCK and BMAL1 activates the expression of CRY, PER, REV-ERB, ROR, and other CCGs (clock controlled genes) through binding to E-box element at their promoters. CRY-PER complex is phosphorylated and transported back to the nucleus inhibiting the CLOCK-BMAL1 activity. PER is phosphorylated to degrade through proteosomal pathway via CK1ε/δ.