Fig. 2.
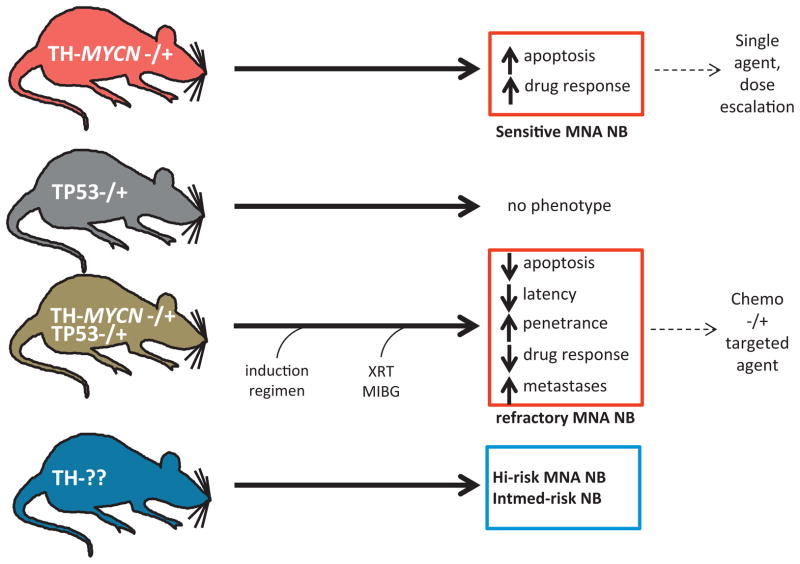
Utilizing TH-driven models of NB to study MYCN-driven oncogenesis and modifier genes. Simple genetic crosses elucidate the functional interdependence of two genes in mice. One example involves the contribution of p53 to the genesis or progression of MYCN-driven tumors. In the crosses above, haploinsufficiency of p53 accelerates NB in the TH-MYCN model. These tumors display defective apoptosis and are resistant to cyclophosphamide. This approach can establish whether specific MYCN targets or cooperating genes are suitable for indirect therapeutic inhibition of MYCN in NB.