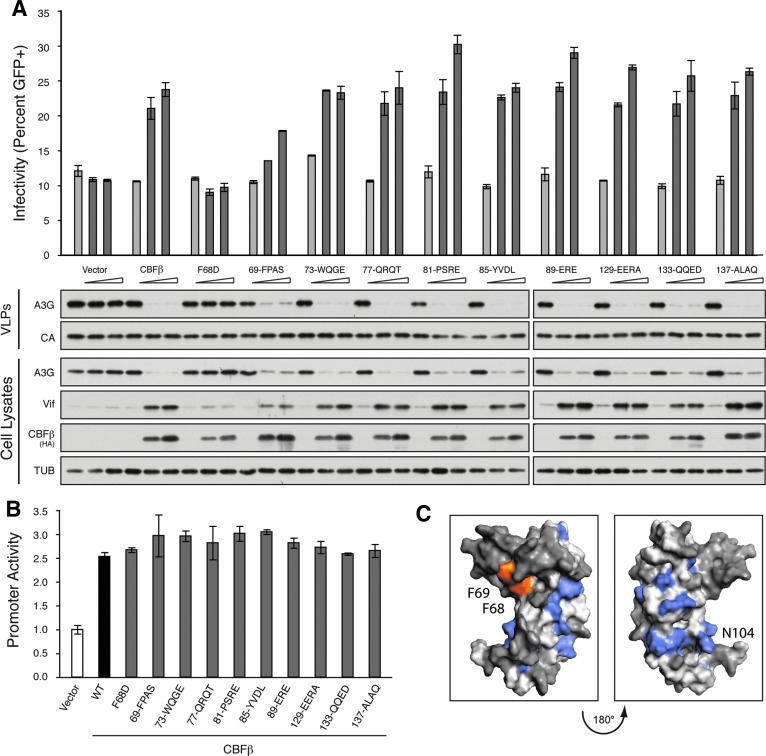
FIG. 3.
Alanine scanning fails to reveal additional residues at the CBFβ/Vif interface. (A) Percent infectivity of HIV-1IIIB measured by infection of CEM-GFP in duplicate and flow cytometry, reported as the mean of the two technical replicates±standard deviation. A constant amount of Vif-proficient A200C HIV-1IIIB molecular clone was cotransfected into a stable CBFβ-knockdown HEK293T cell line with A3G in the presence of an increasing gradient of the indicated CBFβ complementation vector. Representative immunoblots of HA-tagged CBFβ variants, Vif, and A3G in cell lysates and of A3G in HIV-1 particles produced by those cells are shown with their respective tubulin (TUB) and p24 (CA) loading controls. (B) Activity of the FOXP3 promoter reporter gauged by the activity of Firefly luciferase relative to the Renilla luciferase transfection control and reported as the mean±standard deviation of three independent biological replicates, normalized to the no CBFβ vector control (white bar). A constant amount of each luciferase construct was cotransfected with RUNX1 and either empty vector (white bar), HA-tagged CBFβ (black bar), or the indicated HA-CBFβ variant (gray bars) into a stable CBFβ-knockdown HEK293T cell line. (C) CBFβ structural model depicting F68 and F69 (orange), residues that disrupted the RUNX1 heterodimer when altered (blue), and residues that had no impact on either the RUNX1 or Vif interaction when altered (dark gray). The remaining residues (light gray) were not altered in this study.