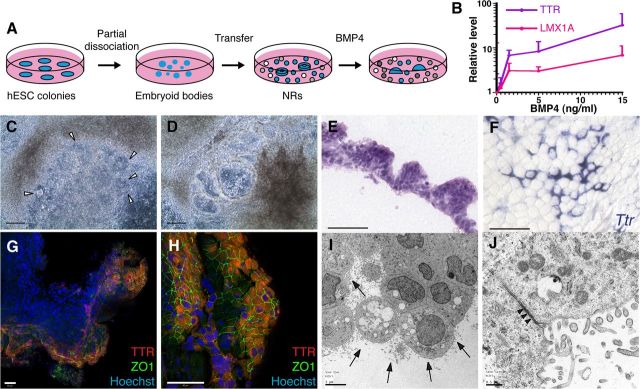
Figure 7.
CPEC differentiation from human ESC-derived NRs. A, Schematic of the NR differentiation method (Zhang et al., 2001). After 16 DIV, NR-containing cultures are treated for 20 DIV with BMP4. B, BMP4 effects on CPEC markers in H9-derived NR cultures (qRT-PCR normalized to no BMP4 controls). Similar induction curves are seen for CPEC genes LMX1A and TTR. C, D, Phase contrast images of H1-derived NR cultures (same field in C and D). In the presence of BMP4, NRs (arrowheads) transform into phase-bright vesicular structures, which eventually form flat epithelial sheets. E, H&E-stained cross section of an H1-derived BMP4-treated colony. The peripheral NR-containing region consists of cells with apical cytoplasm that form a papillary-like tissue reminiscent of endogenous CP. F, ISH of an H9-derived BMP4-treated colony. Strong Ttr expression is evident in epithelial cells toward the colony periphery. G, H, ICC of an H1-derived BMP4-treated colony. Extensive colocalization of TTR and ZO1 occurs at the colony periphery (G and H from two different fields). I, J, Electron microscopy of an H1-derived BMP4-treated colony. Abundant epithelial cells demonstrate extensive lumenal microvilli (arrows), rare cilia, and juxtalumenal tight junctions (arrowheads). Scale bars: C, D, 100 μm; E–H, 50 μm; I, 5 μm; J, 0.5 μm.