Fig. 1.
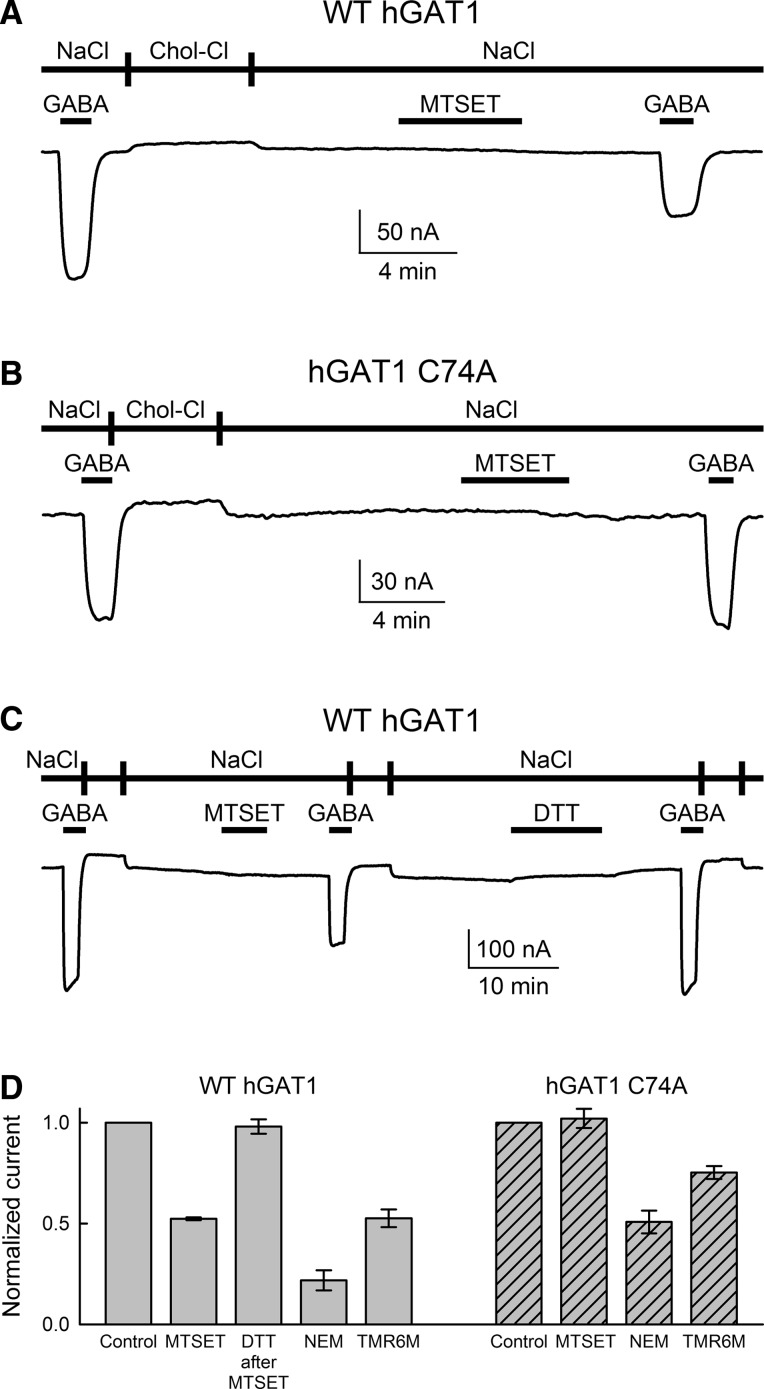
WT GAT1, but not GAT1 C74A, is sensitive to membrane-impermeant sulfhydryl reagents. a A representative GABA-evoked (500 μM) current trace is shown for WT GAT1 before and after labeling with the membrane-impermeant sulfhydryl reagent MTSET. Labeling of GAT1 with MTSET led to ~50 % reduction in the GABA-evoked current. The membrane potential (V m) was −50 mV throughout the experiment. Labeling was carried out at 1 mM MTSET for 5 min in NaCl buffer bathing the oocyte (at 21 ± 2 °C, pH 7.4). b Similar to WT GAT1, GAT1 C74A mediates Na+-dependent and Cl−-facilitated GABA transport (see Fig. 6). Exposure of GAT1 C74A to MTSET (1 mM for 5 min) had no effect on the magnitude of the GABA-evoked (500 μM) current. c Sulfhydryl modification of WT GAT1 with MTSET was completely reversed with DTT. Labeling with MTSET was carried out as in (a), and DTT was applied at 12 mM for 10 min in NaCl buffer. d Summary of data collected from four or more oocytes expressing WT GAT1 or GAT1 C74A. For each experimental condition, the GABA-evoked current obtained after labeling with MTSET, NEM or TMR6M (all at 1 mM for 5 min at −50 mV) was normalized to that prior to sulfhydryl modification in the same cell. Reported values represent the mean ± SE from four or more oocytes. Note that GAT1 C74A is insensitive to the membrane-impermeant MTSET but sensitive to the membrane-permeant NEM. GAT1 C74A was also sensitive to TMR6M