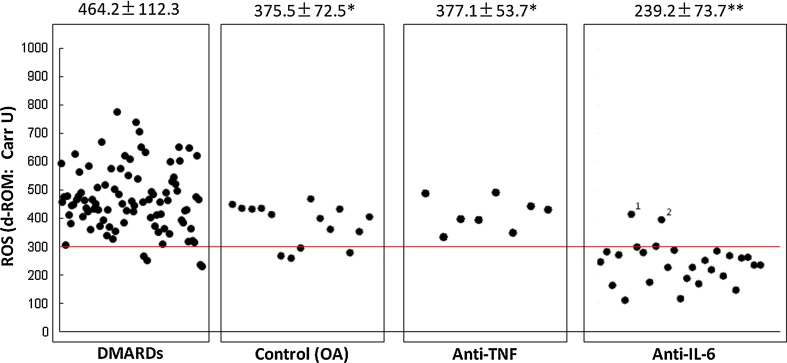
Fig. 1.
Serum levels of oxidative stress are significantly increased in patients with RA. Fifteen patients with OA showed 375.5 ± 72.5 Carr U of ROM, while 91 patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs showed 464.2 ± 112.3 Carr U of ROM, and all but four of these patients showed abnormal levels (>300 Carr U). Levels of ROM were significantly higher in the group of patients with rheumatoid arthritis not treated with biologics, suggesting that oxidative stress is up-regulated in the pathobiology of rheumatoid arthritis. The value of 375.5 ± 72.5 Carr U in the OA group is increased as compared with the normal limit (<300 Carr U). However, this seems to be due to aging. Serum level of oxidative stress markers is significantly low in patients with RA treated with anti-TNF biologics therapy. Serum levels of ROM in 8 patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor-blocking therapy showed 377.1 ± 53.7 Carr U of ROM, and these levels are similar to those in the OA group, suggesting that anti-TNF biologics therapy effectively reduces oxidative stress in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Serum level of oxidative stress is dramatically low in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-IL-6 biologics therapy. Serum levels of ROM in 26 patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with IL-6-blocking therapy showed 239.2 ± 73.7 Carr U of ROM. Only two cases (Cases 1 and 2) showed abnormal levels (408 and 394 Carr U). Furthermore, the C-reactive protein levels of these two cases were not completely suppressed (0.7 and 0.1 mg/dl). On the other hand, the C-reactive protein levels of the 24 cases showing normal levels of ROM were completely suppressed (<0.04 mg/dl). We could confirm that the serum levels of oxidative stress markers are dramatically low in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-IL-6 biologics therapy, suggesting that tocilizumab has a very strong effect of reducing oxidative stress in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. *, **P < 0.05, significantly lower level d-ROM as compared with that in the DMARD group. Results are expressed as the mean ± SD. Between-group differences were assessed by one-way ANOVA test, and a probability <0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance