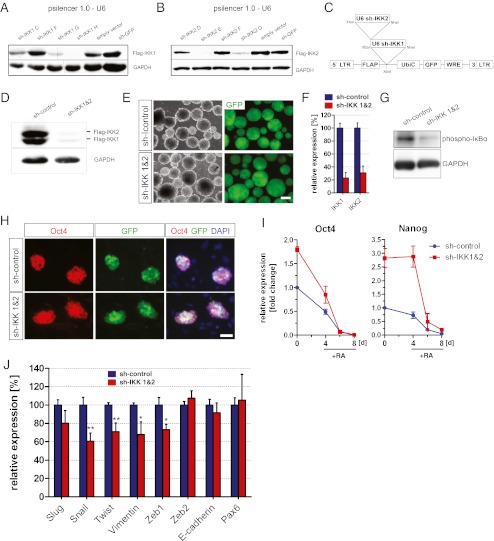
Fig. 3.
Knockdown of IKK1 and IKK2 in ESCs. (a, b) Western blots were carried out after co-expression of flag-tagged IKK1 (a) or IKK2 (b) with the indicated sh-sequences in HEK 293FT cells. (c) Lentiviral vector for inhibition of NF-κB signaling by knockdown of IKK1 and IKK2. LTR, long terminal repeat. WRE, woodchuck post-transcriptional regulatory element. hUbiQ, human Ubiquitin C promoter. U6, murine U6 promoter. (d) Validation of the lentiviral vector. Western blots were performed after ectopic co-expression of Flag-tagged IKK1 and IKK2 together with the lentiviral vector in HEK 293FT cells. (e) J1 ESCs, transduced with the lentiviral vectors indicated, were differentiated as EBs. Scale bar: 200 μm. (f) To validate the knockdown of IKK1 and IKK2, qPCR were carried out after differentiation of ESCs as EBs. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, each performed as triplicate. (g) Knockdown of IKK1 and IKK2 results in reduced levels of phosphorylated IκBα. ESCs were differentiated for 8 days as EBs and treated with RA after 4 and 6 days. Proteins were extracted after 8 days and Western blots were performed. (h) Oct4 stainings of transduced ESCs to confirm maintenance of pluripotency after knockdown of IKK1 and IKK2. Feeder cells were also stained by DAPI, but negative for Oct4 and GFP. Scale bar: 50 μm. (i) Expression levels of oct4 and nanog during differentiation of ESCs as EBs. After 4 days cells were treated with RA. Data indicate mean ± SD of one experiment performed as triplicate representing two independent experiments. (j) Effect of NF-κB inhibition assayed by qPCR. After transduction of J1 ESCs, cells were differentiated as EBs and treated for 4 days with RA. At the day of EB dissociation samples were collected and different markers were assayed. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, each performed as triplicate