FIG. 6.
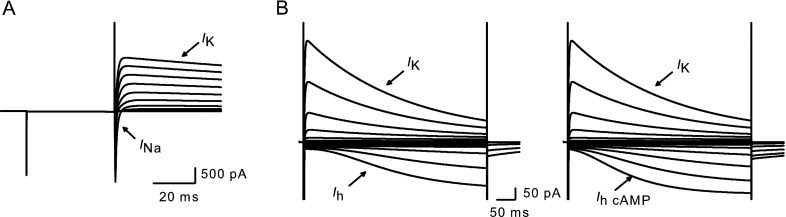
Modeling voltage-dependent current in calyx terminals. A Currents were simulated in response to a voltage protocol from a holding potential of –79 mV, followed by a 40-ms prepulse to −129 mV and subsequent test steps from −89 to +19 mV in 10-mV increments. Rapid inward sodium currents (I Na) and macroscopic outward potassium currents (I K) resemble those described previously (Dhawan et al. 2010). B Longer duration voltage steps (0.5 s) evoke I h at hyperpolarized voltage steps (left). Steps were applied from a holding potential of −79 mV between −149 and −19 mV in 10-mV increments. cAMP in conjunction with I h increased the size and accelerated the activation of the inward currents (right).
