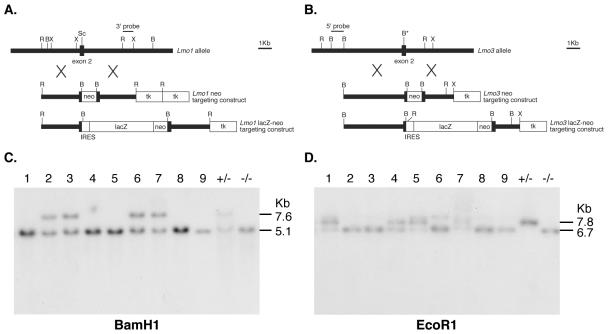
FIG. 2.
Targeted disruption of the Lmo1 and Lmo3 genes. (A) Restriction maps of wild-type Lmo1, neo replacement targeting vector, and lacZ knockin targeting vector. The MC1-neo-pA cassette or an IRES-lacZ reporter was inserted at the ScaI site of Lmo1 exon 2. (B) Restriction maps of wild-type Lmo3, neo replacement targeting vector, and the lacZ knockin targeting vector. The MC1-neo-pA cassette or an IRES-lacZ reporter cassette was inserted into a BamHI site mutagenized into the Lmo3 exon 2. (C and D) Detection of targeted Lmo1 (C) or Lmo3 (D) loci was carried out by filter hybridization using the indicated probes. The Lmo1 targeted allele was detected as a 7.6-kb BamHI fragment, and the Lmo3 targeted allele was detected as a 7.8-kb EcoRI fragment. The results shown were obtained using DNA from pups of a cross between (Lmo1Z/Z; Lmo3+/−) and (Lmo1Z/+; Lmo3−/−) mice. The litter of nine pups at P0 included two pups with the compound null genotype (Lmo1Z/Z; Lmo3−/−) (pups 8 and 9).