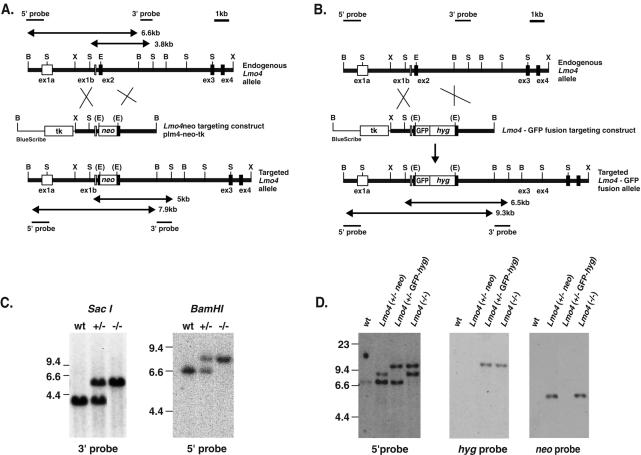
FIG. 5.
Targeted disruption of the Lmo4 gene. (A) Restriction maps of the Lmo4 gene and the BamHI linearized targeting vector plm4-neo-tk, together with the predicted structure of the targeted Lmo4 locus following a homologous recombination event. The black boxes represent coding exons of Lmo4. The expected lengths of the restriction fragments diagnostic for homologous recombination are indicated by double-headed arrows. (B) Restriction maps of the Lmo4 gene and the BamHI-linearized targeting vector plm4GFP-hyg-tk and the predicted structure of the targeted Lmo4 locus following a homologous recombination event are shown. The expected lengths of the restriction fragments diagnostic for homologous recombination are indicated by double-headed arrows. Abbreviations for restriction sites: B, BamHI; S, SacI; X, XhoI; E, EagI. (C) Genotype analysis of mice at P0 derived from an Lmo4+/− × Lmo4+/− intercross. Representative DNA samples from each genotype—i.e., wild-type (wt), heterozygous Lmo4+/−, and homozygous Lmo4 null−/− mice—were digested with SacI, and filter hybridization with the 3′ probe was performed. Wild-type and targeted alleles are 3.8 and 5 kb, respectively. BamHI digestion of the same samples yields fragments of 6.6 (wild-type allele) and 7.9 (targeted allele) kb when hybridized with the 5′ probe which confirms the genotypes. (D) The ES cell line D8 (Lmo4+/−) was subjected to a second round of gene targeting with the linearized vector plm4GFP-hyg-tk. DNA samples from representative ES cell clones of each genotype—Lmo4+/− neo (i.e., the original Lmo4+/− clone with neo inserted into exon 2), Lmo4+/− GFP-hyg (i.e., clone with the original neo mutant allele “re-targeted” by plm4GFP-hyg-tk), and Lmo4−/−—were digested with BamHI and hybridized with the 5′ probe. This yields fragments of 6.6 (wild-type allele) and 7.9 (neo targeted allele) kb in Lmo4+/− neo cells, fragments of 6.6 and 9.3 kb (GFP-hyg targeted allele) in Lmo4+/− GFP-hyg cells, and fragments of 7.9 and 9.3 kb in Lmo4−/− cells. Hybridizing SacI-digested DNA with a neo probe showed only the 5-kb band in Lmo4+/− neo and Lmo4−/− ES cell clones, while rehybridizing the BamHI-digested DNA with the hyg probe yielded only the 7.9-kb GFP-hyg targeted band. Control DNA from the wild-type (wt) ES cell line is also shown. Wild-type, neo targeted, and GFP-hyg targeted alleles are indicated by bands of 6.6, 7.9, and 9.3 kb, respectively.