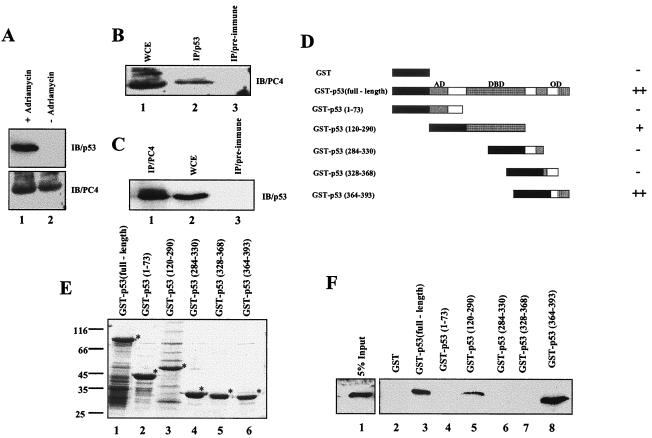
FIG. 2.
PC4 directly interacts with p53 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Induction of p53 expression in the U2OS cell line. The levels of p53 and PC4 present in adriamycin (2 μg/ml)-treated U2OS cells were assessed by Western blotting using anti-p53 (upper panel) and anti-PC4 (lower panel) antibodies. (B and C) In vivo interaction of PC4 with p53. (B) Lane 1, an adriamycin (2 μg/ml)-induced U2OS cell extract was immunoblotted with polyclonal PC4 antibody N17. Lane 2, immunoprecipitation of endogenous PC4 from an induced U2OS cell lysate was performed using anti-p53 monoclonal antibody DO1 followed by immunoblotting with anti-PC4 polyclonal antibody. Lane 3, immunoprecipitation using mouse preimmune serum used as a control. (C) Lane 1, immunoprecipitation of endogenous p53 from an induced U2OS cell extract, using anti-PC4 polyclonal antibody N17 followed by immunoblotting with anti-p53 monoclonal antibody DO1. Lane 2, adriamycin-induced U2OS cell extract immunoblotted with monoclonal p53 antibody DO1. Lane 3, immunoprecipitation reaction with goat preimmune serum used as a control. (D, E, and F) Interaction of PC4 with p53 in an in vitro GST pulldown assay. (D) Schematic representation of GST and GST-p53 fusion proteins. ++, strong interaction of PC4 with respective GST-p53 fusion protein; +, weaker interaction; −, no interaction. (E) SDS-PAGE (10%) and Coomassie blue R250 staining of immobilized GST-p53 fusion proteins. Lane 1, GST-p53 (full length); lane 2, GST-p53(1-73), lane 3, GST-p53(120-290); lane 4, GST-p53(284-330), lane 5, GST-p53(328-368); lane 6, GST-p53(364-393). GST fusion proteins predominantly contain intact proteins (indicated with asterisks) with minimum low-molecular-weight breakdown products. (F) One microgram of GST (lane 2) or GST-p53 fusion proteins (lanes 3 to 8) was incubated with bacterial extract containing 200 ng of PC4 and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PC4 N17 antibody. Lane 1, 5% input of bacterial cell lysate. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot; WCE, whole-cell extract; AD, activation domain; DBD, DNA binding domain; OD, oligomerization domain.