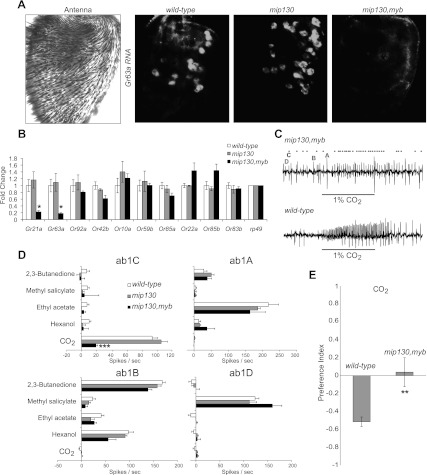
Figure 1.
Myb is required for response to CO2. (A) Whole-mount antennae showing a bright-field microscopy image (left) and Gr63a RNA in situ hybridization (right). Male flies of the following genotypes were used: wild-type (wCanton-S), mip130 mutant (mip1301–36), and mip130,myb double mutant (mip1301–36,mybMH107). (B) qRT–PCR using antennal cDNA of indicated genotypes to measure expression of Or genes found in large basiconic sensilla using rp49 as a normalizer. n = 3 independent experiments per genotype. (C) Representative single-sensillum electrophysiological traces of the ab1 sensillum when wild-type or mip130,myb double-mutant flies were exposed to 1% CO2. Characteristic spikes of the four neurons are indicated by their respective letters (A–D). Each spike belonging to the C neuron is denoted by a black dot in the mutant trace. (D) Electrophysiological responses of the four ab1 neurons to the indicated diagnostic odors. n = 10 recordings per genotype. (E) Preference index to measure behavioral responses of indicated flies to 0.33% CO2 in a T-maze. n = 10 trials per genotype (∼40 flies per trial). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used: (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001.