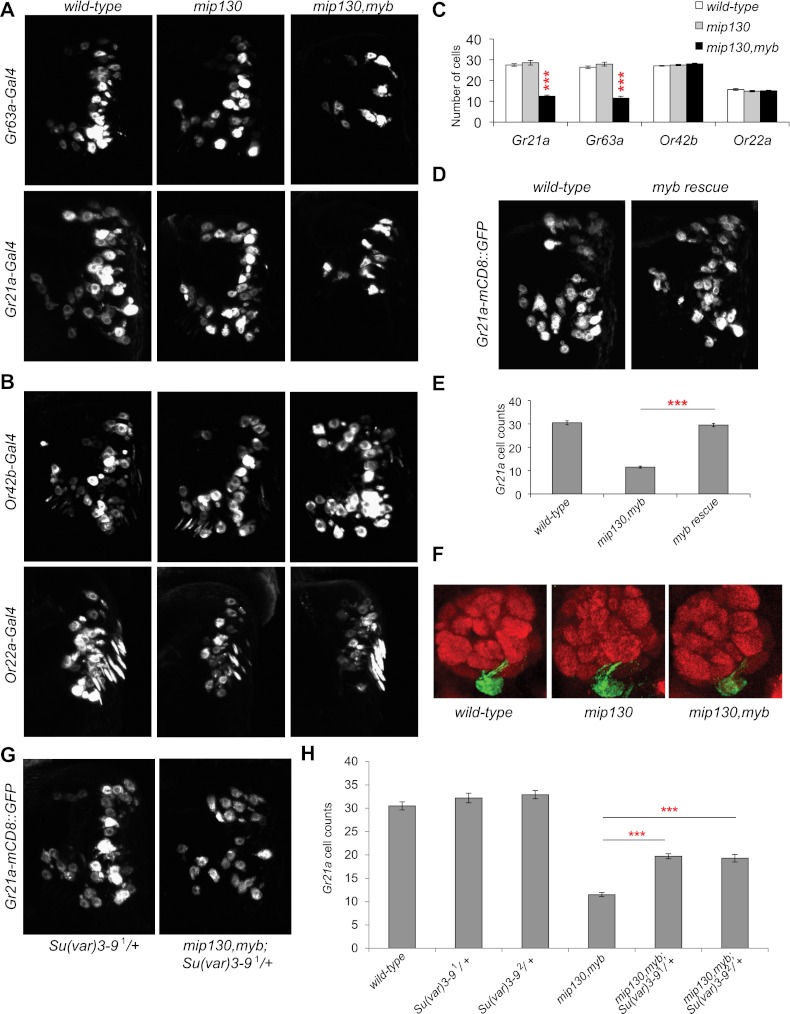
Figure 4.
Promoters of Gr63a and Gr21a are important for Myb regulation (A,B) Whole-mount antennae showing neurons expressing GAL4-responsive membrane targeted GFP (UAS-mCD8∷GFP) with Gr63a or Gr21a promoter-GAL4s (A) or controls, Or42b or Or22a promoter-GAL4s (B), in wild-type, mip130 mutant, and mip130,myb double mutant. (C) Counts of GFP+ cells for A and B. n = 10 per genotype. (D) Whole-mount antennae showing neurons expressing a different Gr21a promoter direct fusion transgene (Gr21a promoter-mCD8∷GFP) and myb rescue (mip130,myb; Gr21a promoter-mCD8∷GFP/elav-GAL4; UAS-RFP∷myb+). (E) Counts of GFP+ cells for D. n = 10 per genotype. (F) Immunofluorescence using anti-GFP (green) and anti-nc82 (neuropil marker; red) antibodies on antennal lobes of wild-type, mip130 mutant, and mip130,myb double mutant with Gr63a-GAL4; UAS-mCD8∷GFP. (G) Whole-mount antennae showing neurons expressing Gr21a promoter-mCD8∷GFP in Su(var)3-91/+ and mip130,myb;Su(var)3-91/+. (H) Counts of GFP+ cells for G and Su(var)3-92, a second null allele. n = 10 per genotype. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-tailed Student's t-test was used: (***) P < 0.001.