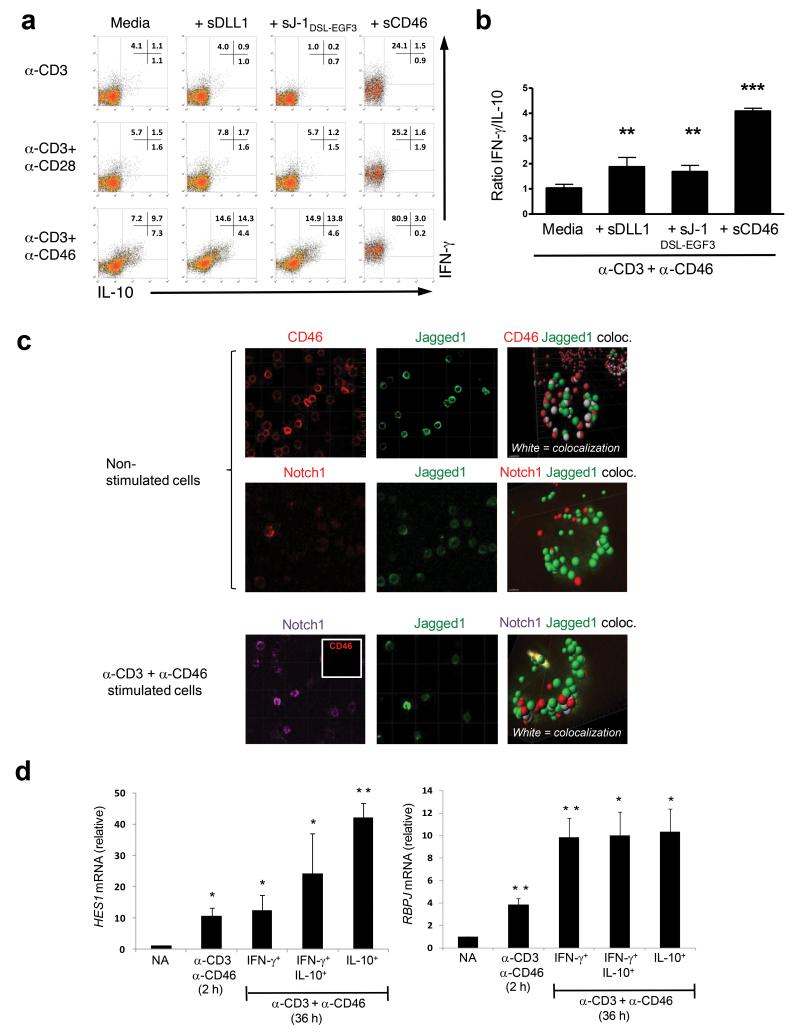
Figure. 4. Undisturbed CD46 and Notch system crosstalk is required for normal IFN-γ to IL-10 switching in human TH1 cells.
(a) Addition of sDLL1, sJ-1DSL-EGF3 or sCD46 during CD3, CD3+CD28 or CD3+CD46 activation of CD4+ T cells increases the numbers of IFN-γ-secreting TH1 cells and (b) changes the IFN-γ:IL-10 ratio of cytokines secreted into the media. Results shown are mean ± SD (n = 6). (c) CD46 sequesters Jagged1 on resting T cells and prevents the Jagged1 and Notch1 interaction. Non-activated (upper two rows of panels) or CD3+CD46-activated (lower row of panels) T cells were stained with antibodies to CD46, Notch1 or Jagged1 and then subjected to superresolution confocal microscopy and 3D analysis to assess for molecular co-localization. White areas in the 3D analyses indicate co-localization of assessed proteins. CD3+CD46-activated T cells lose CD46 surface expression and become negative for CD46 staining (see insert in left panel, lower row). Shown are representative results of two independently performed experiments. (d) CD46 co-stimulation of purified CD4+ T cells increases HES1 and RBPJ mRNA transcription. T cells were activated as indicated and the three emerging IFN-γ- and IL-10-secreting populations from the 36hr sample cell sorted. mRNA was purified and then subjected to quantitative PCR analysis for HES1 and RBPJ transcripts. Expression of mRNA is presented relative to 18s mRNA expression in each sample. Data represent mean ± SD (n=3). *, p < 0.05 **, p < 0.005, ***, p < 0 .001 when compared to media (b) or non-activated cells (d).