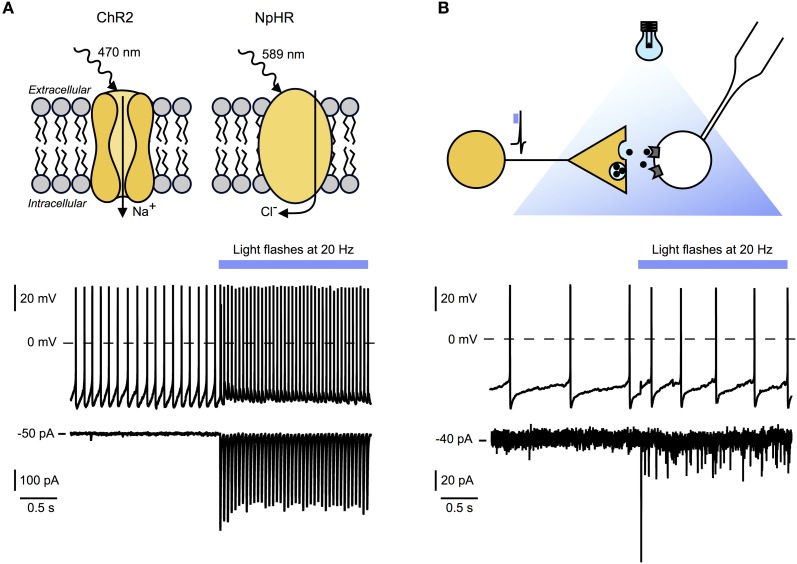
Figure 2.
Optogenetic tools for circuit mapping and functional characterization of synaptic signaling modes. (A) Top panel: Example of light activated excitatory and inhibitory optogenetic tools. Channelrhodopsin 2 (ChR2) is a sodium channel sensitive to blue light. Targeted to specific cell types it causes fast (millisecond scale) depolarization and stimulation of action potentials in these cells. Halorhodopsin (NpHR) is a light activated chloride pump which causes hyperpolarization and suppression of action potential firing in target neurons. Bottom and middle panel: Whole-cell recordings of an hcrt/orx neuron expressing ChR2 before and during 20 Hz optical stimulation (blue bar). Bottom: Voltage clamp recording showing time locked currents evoked by blue light flashes. Middle: Current clamp recording with baseline firing rate and time locked action potential firing during optical stimulation. (B) Top panel: Experimental scheme illustrating experimental setup for ChR2-assisted circuit mapping. Yellow neuron, expressing ChR2, will release signaling molecules after optical stimulation. Time locked responses in postsynaptic cell (white) can be recorded using whole-cell patch-clamping. In combination with pharmacological blockade this technique allows the determination of receptors and transmitters involved. Bottom and middle panel: Recordings of a histamine neuron responding to 20 Hz optogenetic stimulation of hcrt/orx fibers (blue bar). Bottom: Voltage-clamp recording showing time locked postsynaptic currents evoked by transmitters release from hcrt/orx terminals in response to blue light flashes. Failures indicate that not all action potentials lead to vesicle release. Middle: Current-clamp recording with baseline firing rate and increased action potential firing during optical stimulation of hcrt/orx fibers.