Abstract
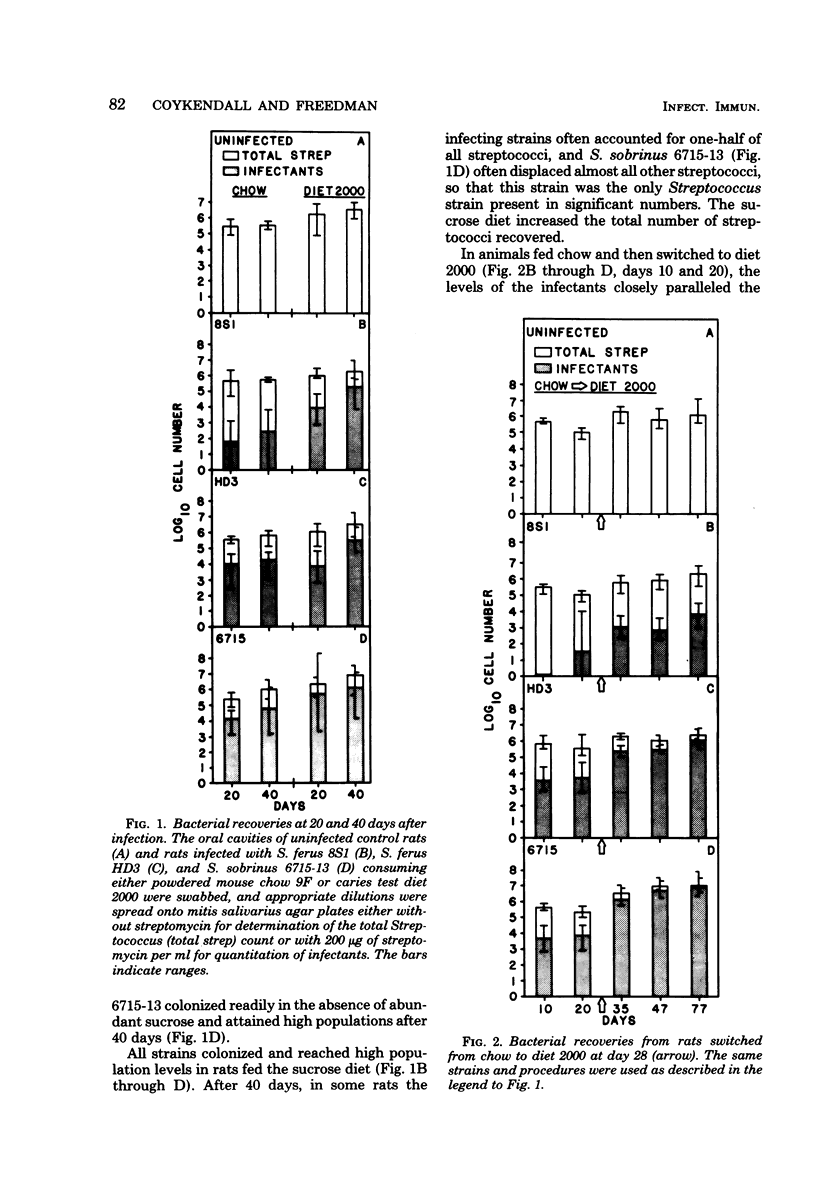
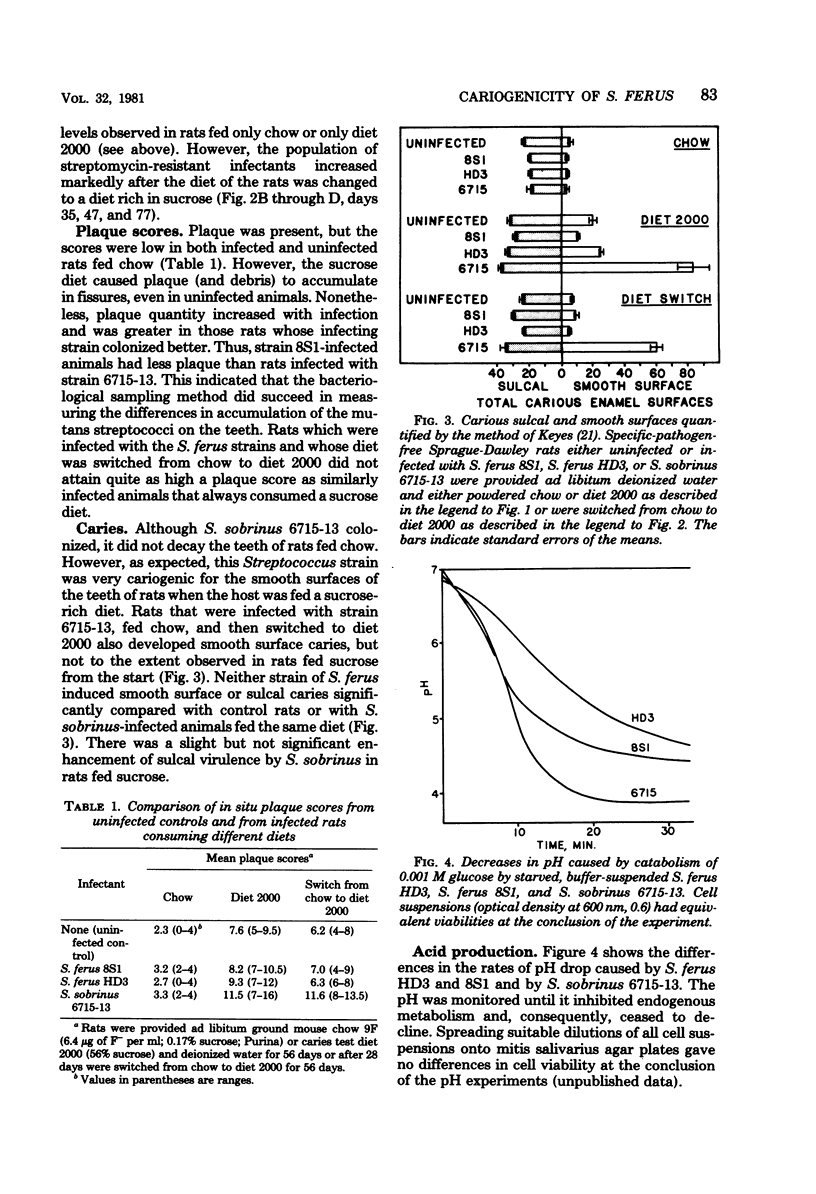
Streptococcus ferus, which is indigenous to wild rats, is a member of the mutans group of streptococci. We tested its ability to colonize and to cause caries in laboratory rats by comparing two strains of S. ferus with the very cariogenic Streptococcus sobrinus strain 6715. Groups of rats were fed either finely ground mouse chow or a 56% sucrose diet, or they were switched from chow to the sucrose diet. All three strains colonized the mouths of rats regardless of diet. However, the infectants reached higher proportions of the total flora more quickly in the rats consuming sucrose. Similarly, the percentage of the oral flora represented by an infecting organism increased numerically when rats originally fed chow were switched to the sucrose diet. S. ferus formed plaques on the teeth of the rats, but these plaques did not proliferate over smooth tooth surfaces as extensively as did those of S. sobrinus. Although S. ferus colonized and accumulated, it was non-cariogenic in rats fed sucrose compared both with rats fed similarly but infected with S. sobrinus 6715 and with uninfected controls. In vitro measurements suggested the S. ferus produced acid less rapidly than S. sobrinus. Thus, the lack of cariogenicity in S. ferus may result from an inability to form copious plaques on smooth tooth surfaces and from low acid production and, therefore, may represent a natural absence of the pathogenic potential usually inherent in the mutans streptococci.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. E., Moore W. J. Distribution of dental caries in ancient British populations. IV. The 19th century. Caries Res. 1976;10(6):401–414. doi: 10.1159/000260233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Bratthall D., O'Connor K., Dvarskas R. A. Serological and genetic examination of some nontypical Streptococcus mutans strains. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):667–670. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.667-670.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coykendall A. L., Specht P. A., Samol H. H. Streptococcus mutans in a wild, sucrose-eating rat population. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.216-219.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stoppelaar J. D., Van Houte J., Backer Dirks O. The relationship between extracellular polysaccharide-producing streptococci and smooth surface caries in 13-year-old children. Caries Res. 1969;3(2):190–199. doi: 10.1159/000259582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. B., Melville T. H. Fermentation end-products of cariogenic and non-cariogenic streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 May;13(5):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Coykendall A. L. Variation in internal polysaccharide synthesis among Streptococcus mutans strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):475–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.475-479.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M., Birked D., Granath K. Analyses of glucans from cariogenic and mutant Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):17–27. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.17-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B., Schroeder H. E. Biochemical and morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides produced by cariogenic streptococci. Helv Odontol Acta. 1967 Oct;11(2):131–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Streptococci of dental plaques. Caries Res. 1968;2(2):147–163. doi: 10.1159/000259553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy E. M. Characteristics of some extra-cellular, polysaccharide-producing, oral streptococci from Tokelauan Islanders. N Z Dent J. 1974 Apr;70(320):118–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Kotani S. Demonstration of serotype d and g specificities of Streptococcus mutans by immunodiffusion. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):495–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. D. Lactate dehydrogenase mutants of Streptococcus mutans: isolation and preliminary characterization. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.206-212.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Sandham H. J., Bradley E. L., Jr Changes in Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli in plaque in relation to the initiation of dental caries in Negro children. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Apr;18(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYES P. H. Dental caries in the molar teeth of rats. II. A method for diagnosing and scoring several types of lesions simultaneously. J Dent Res. 1958 Nov-Dec;37(6):1088–1099. doi: 10.1177/00220345580370060901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B., Jordan H. V., Edwardsson S., Svensson I., Trell L. The occurrence of certain "caries-inducing" streptococci in human dental plaque material with special reference to frequency and activity of caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Aug;13(8):911–918. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton N. W., Kakehashi S., Fitzgerald R. J. Recovery of specific "caries-inducing" streptococci from carious lesions in the teeth of children. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 May;15(5):461–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel I. D. Dental caries. Am Sci. 1979 Nov-Dec;67(6):680–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M. Essential dependence of smooth surface caries on, and augmentation of fissure caries by, sucrose and Streptococcus mutans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.526-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L., Fitzgerald R. J., Larson R. H. Diminished virulence of glucan synthesis-defective mutants of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.197-203.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer J. M., Krichevsky M. I., Keyes P. H. The metabolic fate of glucose catabolized by a washed stationary phase caries-conducive streptococcus. Caries Res. 1969;3(2):167–177. doi: 10.1159/000259580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods R. A dental caries susceptibility test based on the occurrence of Streptococcus mutans in plaque material. Aust Dent J. 1971 Apr;16(2):116–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.1971.tb02314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Burgess R. C., Onose H. Oral implantation of human strains of Streptococcus mutans in rats fed sucrose or glucose diets. Arch Oral Biol. 1976;21(9):561–564. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(76)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Houte J., Duchin S. Streptococcus mutans in the mouths of children with congenital sucrase deficiency. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Nov;20(11):771–773. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


