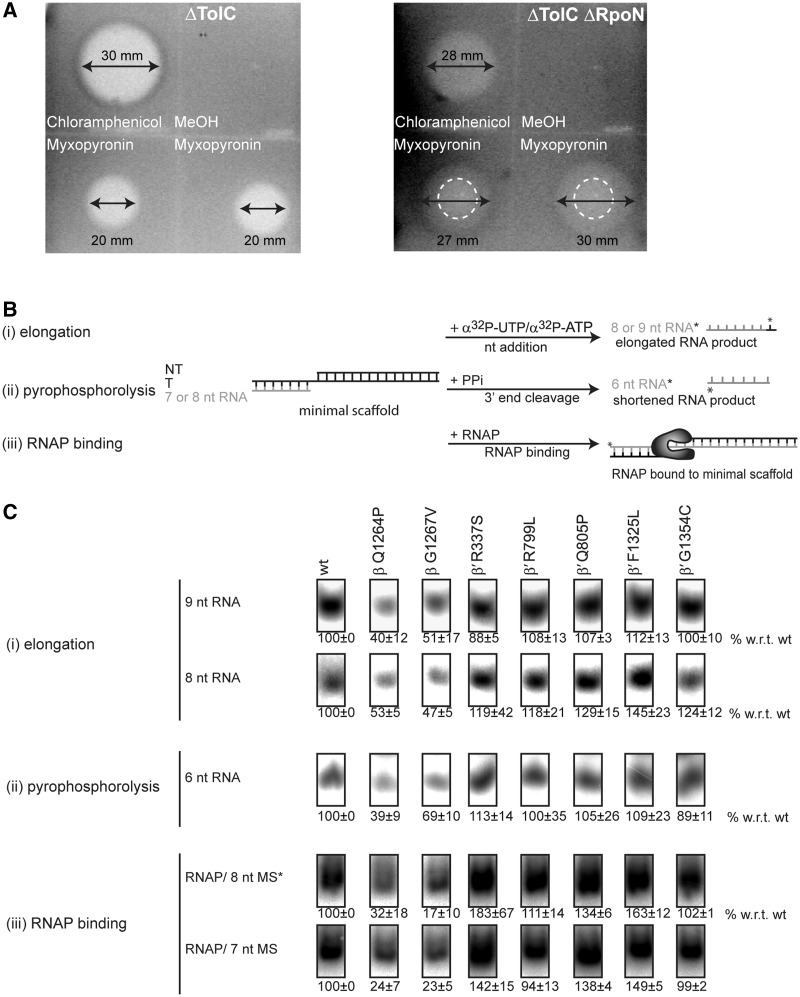
Figure 2.
Myxopyronin sensitivity in vivo and switch 3 mutants have reduced DNA template affinity. (A) Zone of inhibition assays. The loss of RpoN increases sensitivity to myxopyronin. Myxopyronin inhibits growth of the ΔTolC strain within a zone of 20 mm. The zone of inhibition (27–30 mm, indicated by arrows) for the ΔTolC ΔRpoN strain was defined as a combination of a central zone with no growth (15 mm, dashed circle) plus a ring of impaired growth. (B) Schematic of the (i) minimal scaffold (extension of an RNA hybridized to DNA by a single labelled nucleotide), (ii) pyrophosphatase (shortening of a 5′-end-labelled RNA upon addition of PPi) and (iii) minimal scaffold binding (binding of RNAP to the minimal scaffold containing a 5′-end-labelled DNA template strand) assay. (C) The switch 3 mutants, β-Q1264P and β-G1267V are significantly reduced in supporting RNA extension, (top), in cleaving the terminal nucleotide (middle) and in binding the minimal scaffold (bottom). Assays were titrations at three concentrations (25, 50 and 100 nM RNAP) and activity was calculated relative to the wild-type (wt) at the respective concentrations (100%). The numbers reflect the activity obtained as an average from the three concentrations and the error bars are standard deviations.