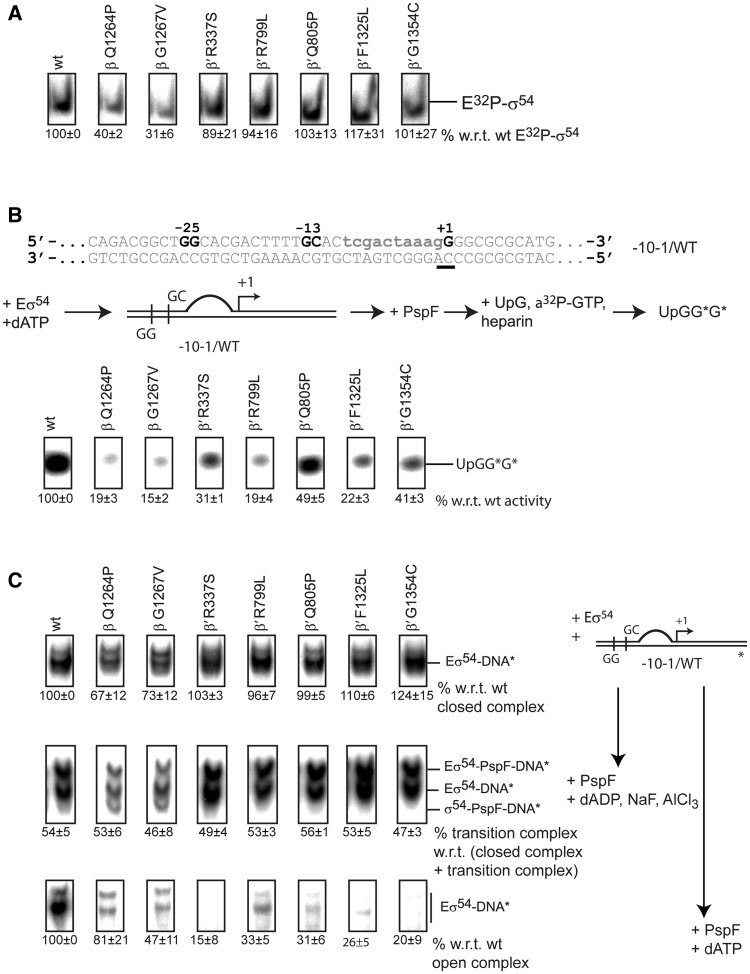
Figure 3.
The switch 1, 2, 4 and 5 mutants are defective in RPo formation. (A) EMSA with 32P-σ54. Complex formation of E32P-σ54 was measured as a supershift with respect to unbound 32P-σ54. The switch 3 mutants, β Q1264P and β G1267V, are defective in forming E32P-σ54. (B) Top: spRNA assay using a linear template representing the nifH promoter with a preformed transcription bubble (mismatch indicated in lower case). The start site is underlined. Middle: The spRNA assay: the RPc was incubated with PspF + dATP followed by an extension mix of UpG primer, heparin and α-32P-GTP (guanosine triphosphate). Labelled (UpGGG*) was measured. Bottom: Reduced accumulation of extended UpG species indicated significant defects in supporting promoter-directed transcription for all mutants. (C) Right: Schematic of the three binding reactions. Eσ54 was incubated with DNA only to form RPcs (top), with DNA, PspF and ADP·AlF to form RPis (middle) or with DNA, PspF and ATP to form RPos. Left: Switch 3 mutants, β-Q1264P and β-G1267V, are reduced in RPc formation (top). Approximately 50% of all RPcs shift into the trapped RPi state confirming that all variants interact with PspF (middle). RPo formation is severely affected in all mutants (bottom). For open and trapped complexes, 200 µg/ml heparin was added for 5 min to outcompete non-specific binding interactions.