Figure 1.
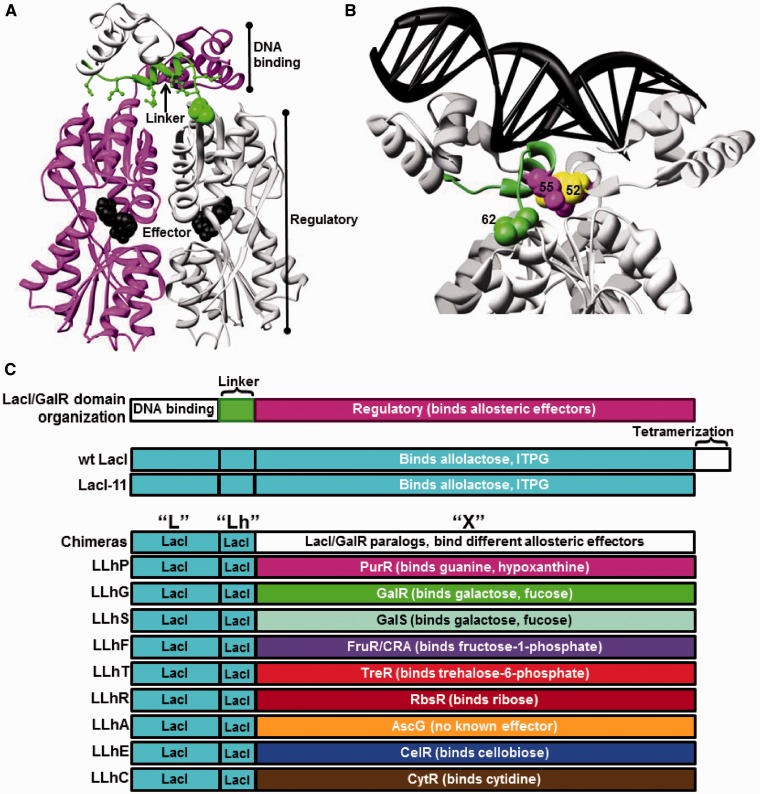
Structure of a representative LacI/GalR protein and schematic of chimeric homologs. Dimeric LacI (8) (pdb 1efa) illustrates the structure common to LacI/GalR homologs. (A) The protein is oriented to show the two monomers (magenta and light gray) and one linker (green). DNA-binding domains are at the top of the structure, and effector ligand (black spheres) is bound in the clefts of the regulatory domains. Non-conserved linker positions that interact with the regulatory domains are shown with green ball-and-stick. Position 62 is highlighted with green spheres. (B) The protein structure is rotated and zoomed to show bound DNA (black ladder) and the side chains of positions 52 (yellow), 55 (magenta) and 62 (green). Structure depictions were created using UCSF Chimera (89). (C) Cartoon depiction of domain compositions for LacI/GalR homologs and chimeras. Chimeric proteins comprise the DNA-binding domain and linker of LacI joined to the regulatory domains of nine natural homologs (Table 1). LLhP was previously reported in (12). LLhG and LLhG/E62K were previously reported in (13). A C-terminal, 11 amino acid deletion of the tetramerization domain in wild-type LacI results in a dimeric version (23,90).