Fig. 3.
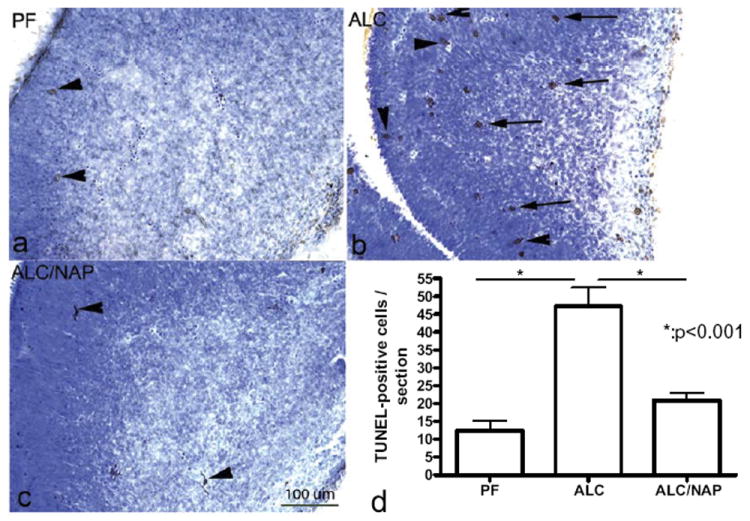
Prenatal alcohol exposure increases the number of TUNEL positive cells in basal ganglia eminence of E13 fetal brains (b) as compared with control group (a). Administration of NAP alongside alcohol exposure prevented alcohol-induced increases in TUNEL-positive cells (c). Scale bar=200 μm. The one-way ANOVA demonstrated a significant difference between groups (P=0.0005). Increases in TUNEL-positive cells were found in the ALC group as compared with the PF group (P<0.001) (d). Importantly, NAP administration alongside alcohol exposure prevented a significantly alcohol-induced increase in TUNEL-positive cells (P<0.001) (d). Values shown as means±SEM. N=5 for each group (PF, ALC, and ALC/NAP).
