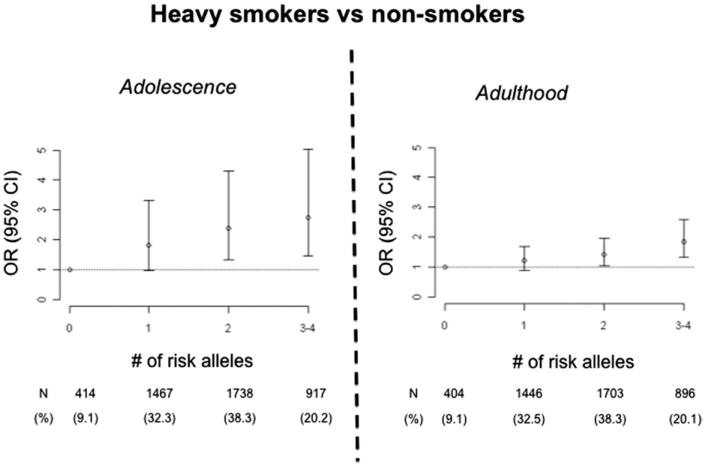
Fig. 5.
Additive effects of the TTC12–ANKK1–DRD2 and CHRNA5–CHRNA3–CHRNB4 gene clusters on smoking behavior in adolescence and adulthood. Risk of heavy smoking increases linearly with the number of risk alleles at the two loci. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). (Adapted from Ducci F, Kaakinen M, Pouta A, et al. TTC12–ANKK1–DRD2 and CHRNA5–CHRNA3–CHRNB4 influence different pathways leading to smoking behavior from adolescence to mid-adulthood. Biol Psychiatry 2011;69(7):650–60.)