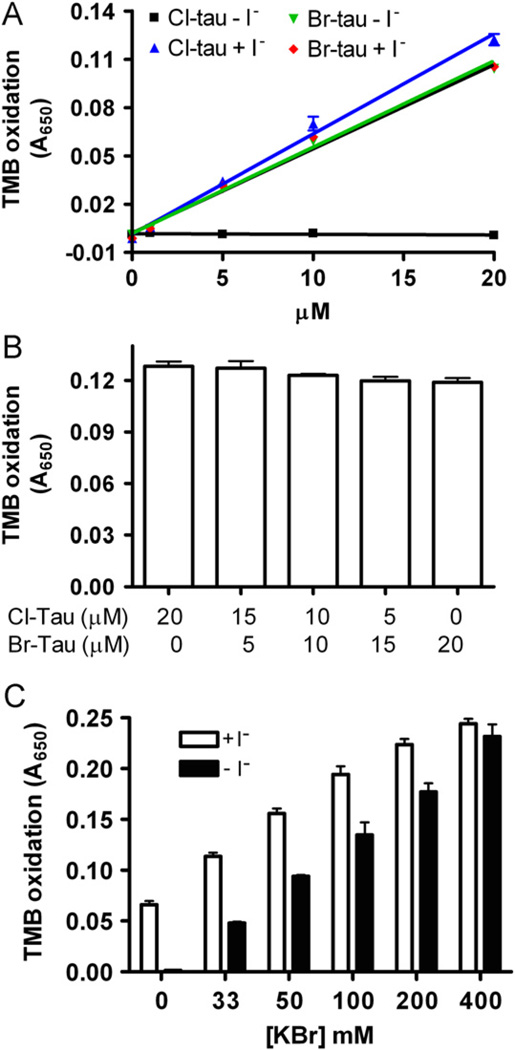
Fig. 2.
VPO1-mediated HOBr and HOCl generation at physiological concentrations of chloride and bromide. (A) Oxidation of TMB by Cl-tau and Br-tau in the absence or presence of I−. The experiments were carried out by adding Cl-tau and Br-tau (as indicated) into TMB solution ± I− (5 mM). After 5 min, absorbance at 650 nm was recorded. (B) Oxidation of TMB by mixture of Cl-tau and Br-tau in the presence of I−. The concentrations of Cl-tau and/or Br-tau were sustained at 20 µM. (C) Oxidation of TMB by VPO1-mediated HOCl and HOBr at physiological concentrations. One hundred microliters of reaction containing 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, 50 µM H2O2, 5 mM taurine, and 100 nM rVPO1, 140 mM NaCl, and 0–400 µM KBr was carried out at 37 °C for 30 min. The reaction was stopped by adding catalase (25 µg/ml). The stopped reaction was then mixed with developing agent in the presence or absence of I−. After 5 min, absorbance at 650 mm was recorded. The data are from three independent experiments. Error bars, SD.