Figure 1. Zinc deficiency-induced inhibition of tubulin polymerization in IMR-32 cellsis reverted by NAC and LA.
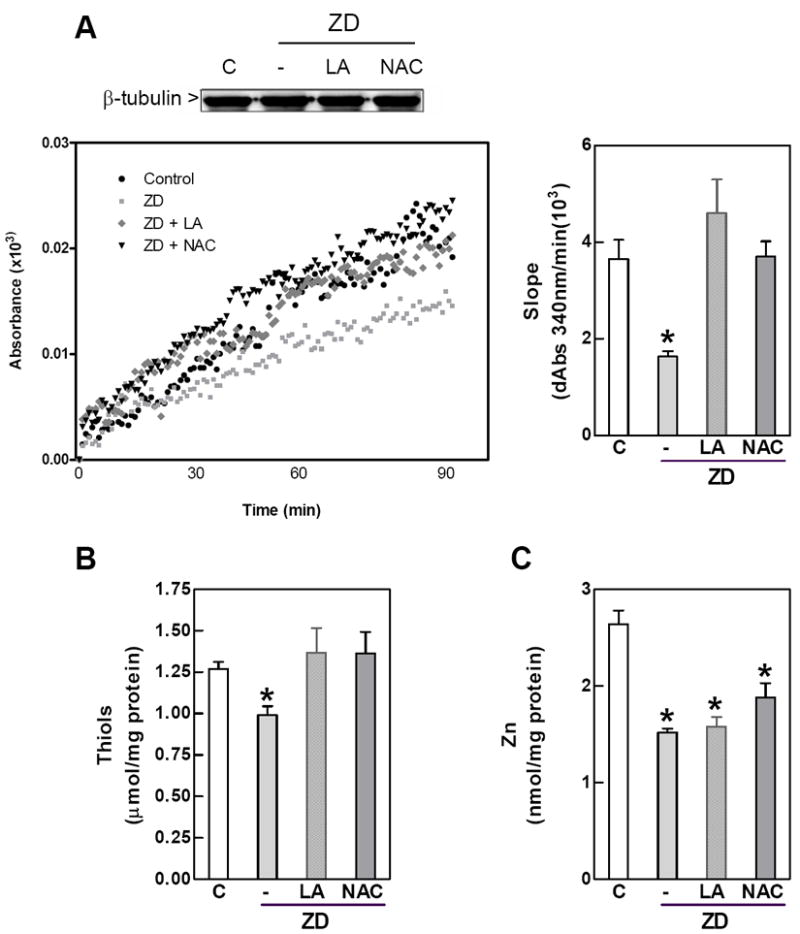
IMR-32 cells were incubated for 24 h in control non-chelated media (C) or in chelated media containing 1.5 μM Zn (ZD) without or with the addition of 0.5 mM LA (LA) or 1mM NAC (NAC). 100,000 × g supernates were prepared as described under Materials and Methods. A- In vitro tubulin polymerization. Left panel shows a representative kinetics. Tubulin polymerization rates were calculated as the slope in the initial linear phase of the polymerization (right panel).; B- Zinc concentration and C- protein thiol concentration in 100,000 × g supernatants Results are shown as means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. *Significantly different compared with the other groups (p<0.05, one-way ANOVA test).
