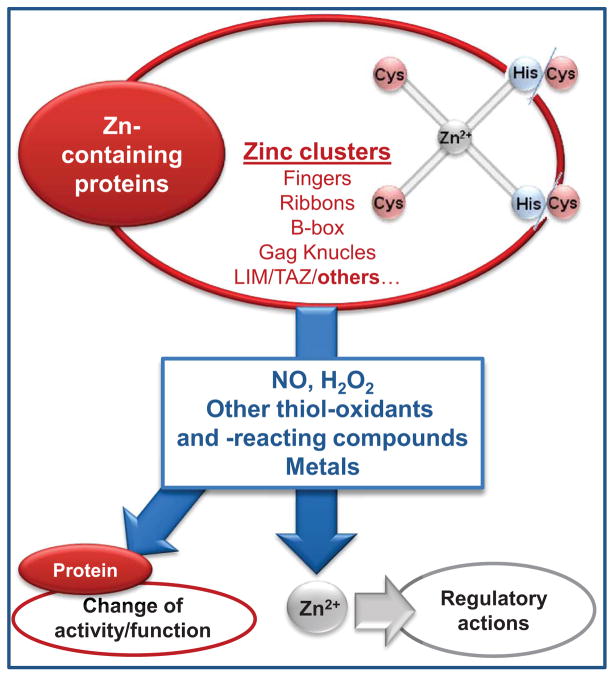
Figure 5. Release of zinc from zinc-sulfur binding domains.
Zinc can bind tetrahedrally to binding domains in proteins through Cys4 or Cys2His2 interactions. Different molecules including NO, H2O2, oxidized GSH, metals, and molecules that react with thiols or have the capacity to oxidize them, cause the release of free zinc. The released zinc can have different regulatory actions, while the modified protein may or may not undergo changes in activity/function.