Figure 1.
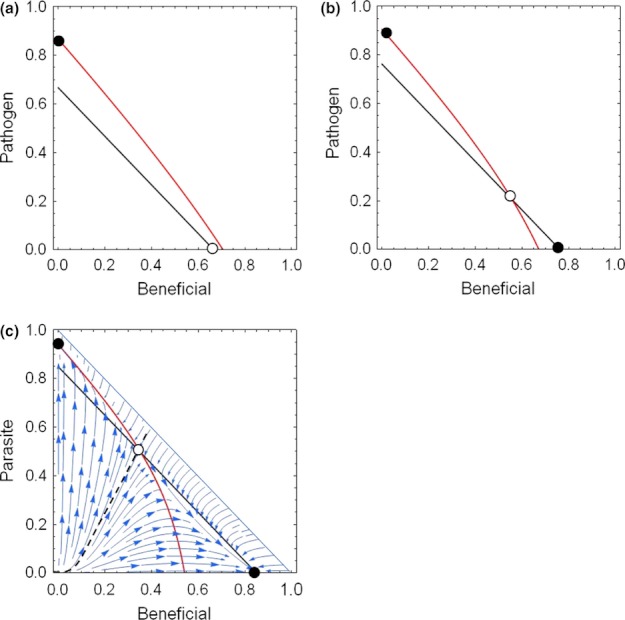
The emergence of bistability as host resource levels Is increase (eqn 3). The higher the host resource input rate Is, the steeper the Pathogen's nullcline (grey, red online) (A: Is= 5; B: Is= 7; C: Is= 11; black is the Beneficial's nullcline). The system becomes bistable above a critical Is value. Solid dots indicate stable fixed points, and the empty dot indicates the unstable fixed point (rp= 2.5, rb= 2, α = 0.2, k = 1, Ac= 0.1). The antibiotic effect of beneficials on pathogens is scaled by 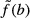 , which is a function of
, which is a function of 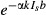 . Increasing Is increases growth rates of all bacteria but also allows greater antibiotic production, leading to suppression of Pathogens.
. Increasing Is increases growth rates of all bacteria but also allows greater antibiotic production, leading to suppression of Pathogens.
