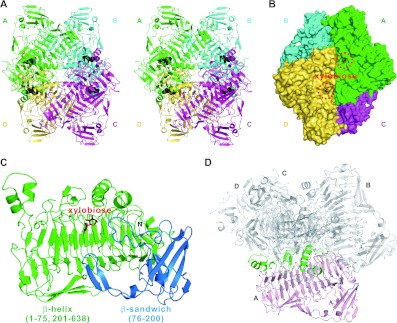
Figure 1. The overall structure of XylC—xylobiose.
(A) Stereo view of the tetrameric XylC–xylobiose structure. The four monomers are depicted in green, cyan, magenta and yellow; the xylobiose molecules are shown in black sphere representation. (B) Surface representation of XylC. (C) Two different domains (parallel β-helix in green and β-sandwich domain in blue) of a XylC monomer. (D) The regions from the parallel β-helix domain in green (residues 53–59, 276–305, 449–466, 509–519 and 584–596) and one small loop from the β-sandwich domain in blue (residues 177–179) are involved in the tetramer interactions.